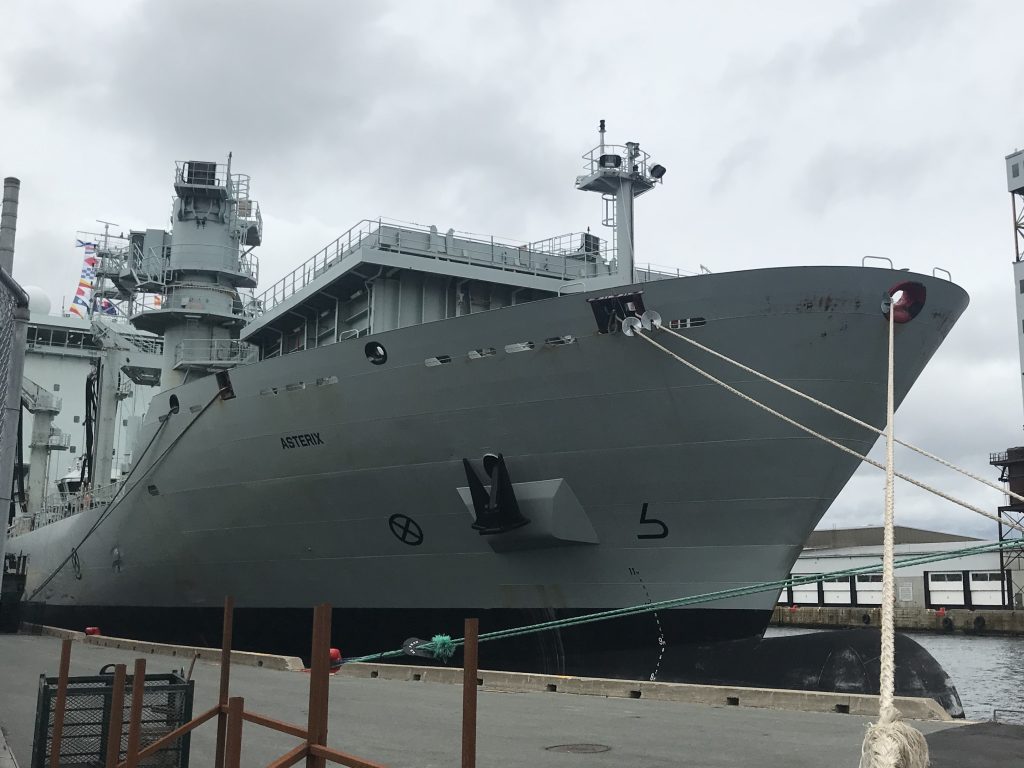

As part of Defsec Atlantic, Federal Fleet and Hepburn Engineering, the Toronto based company that supplied the RAS gear were offering tours of the ship at Pier 23.
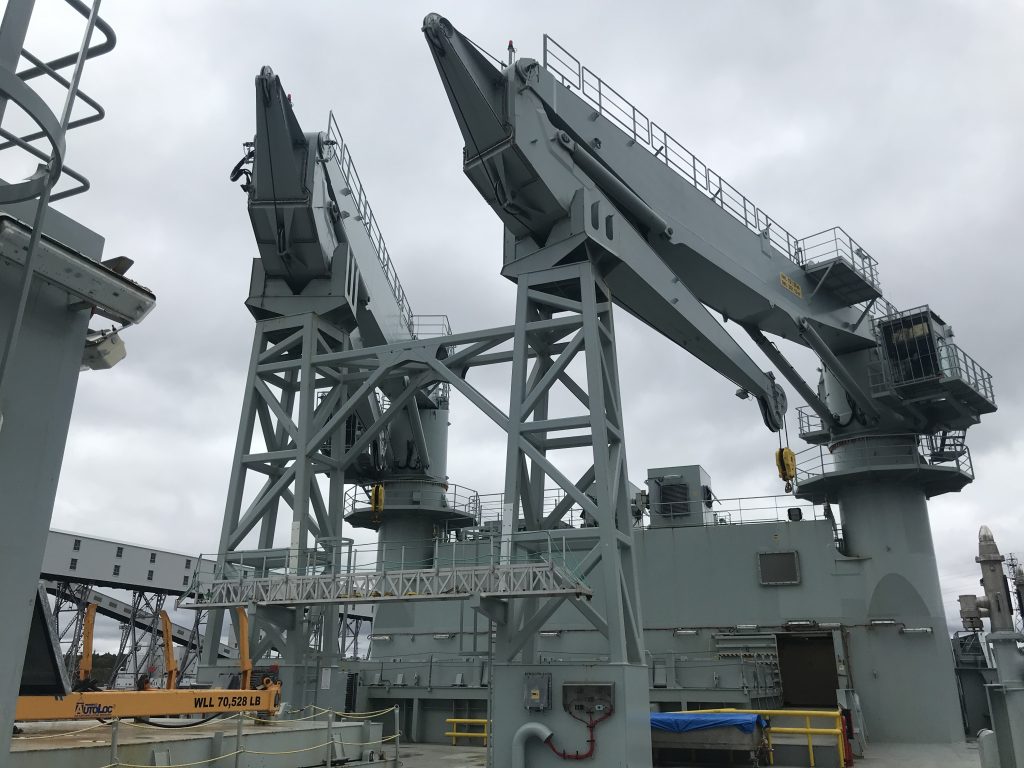
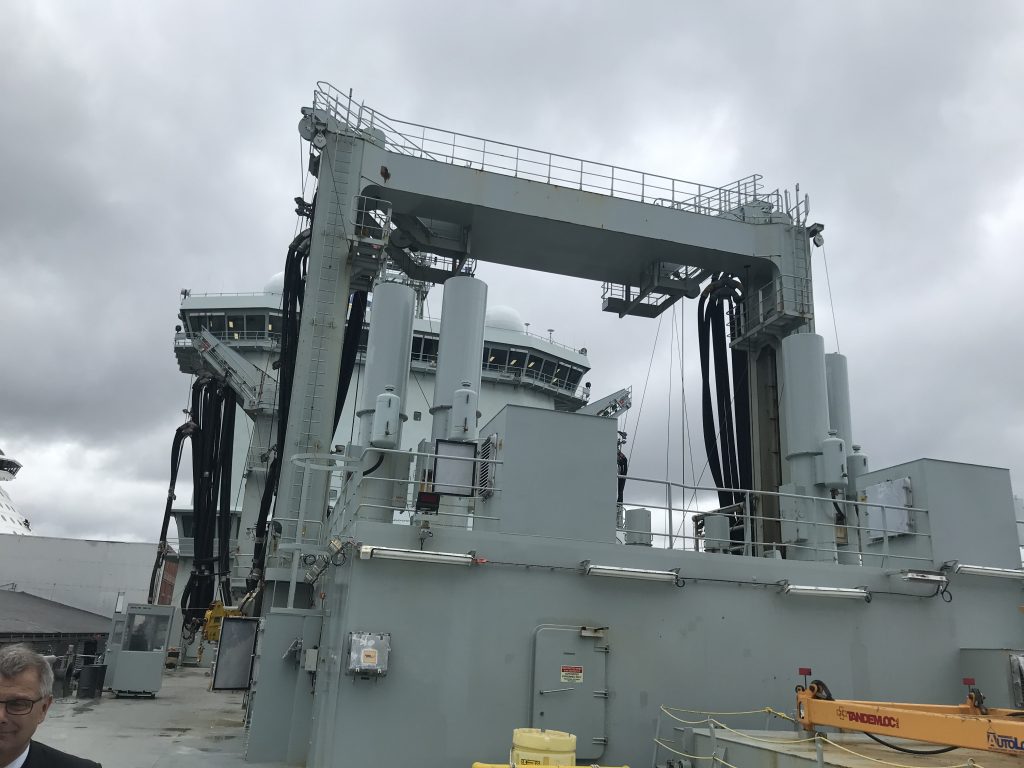
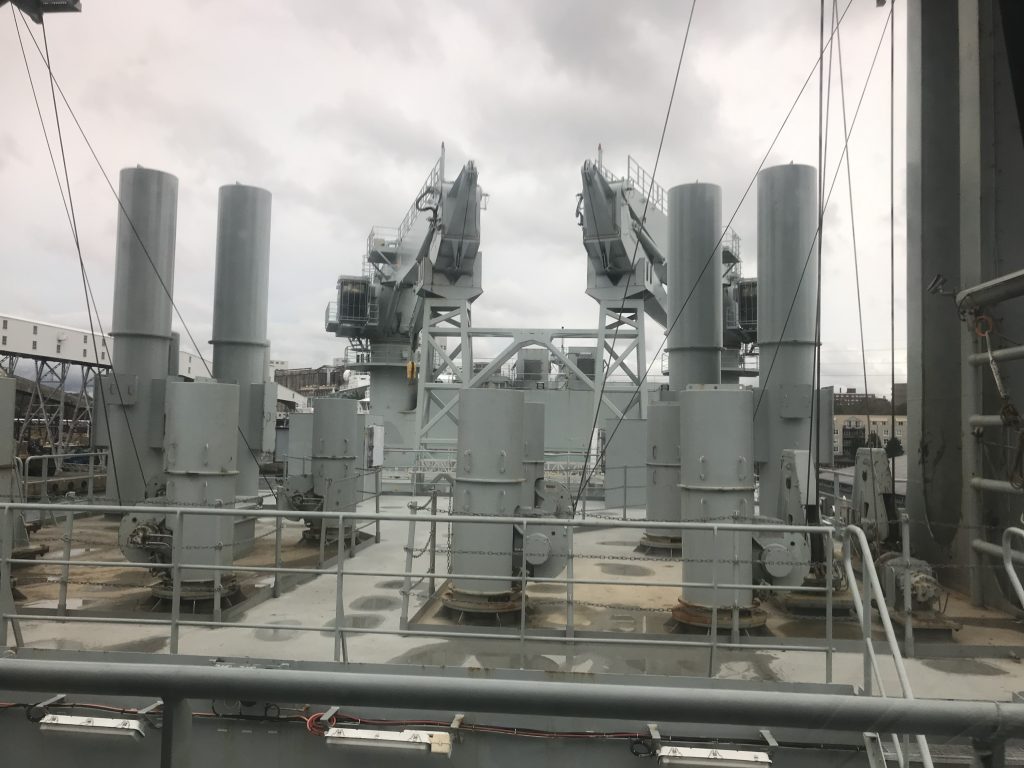
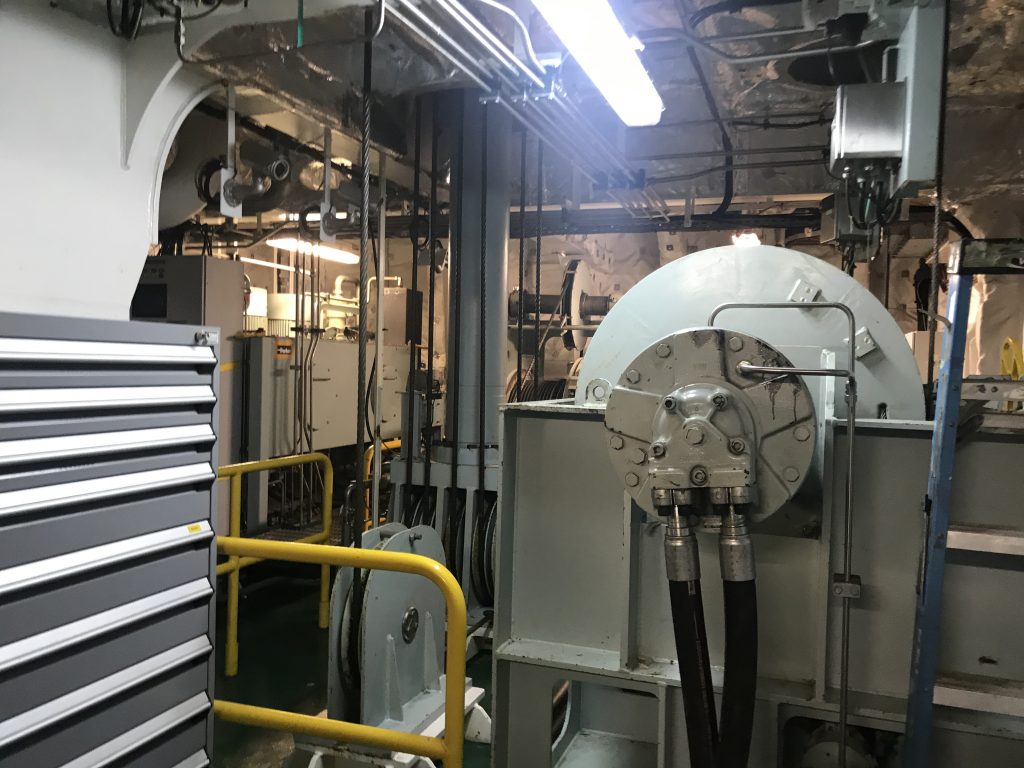
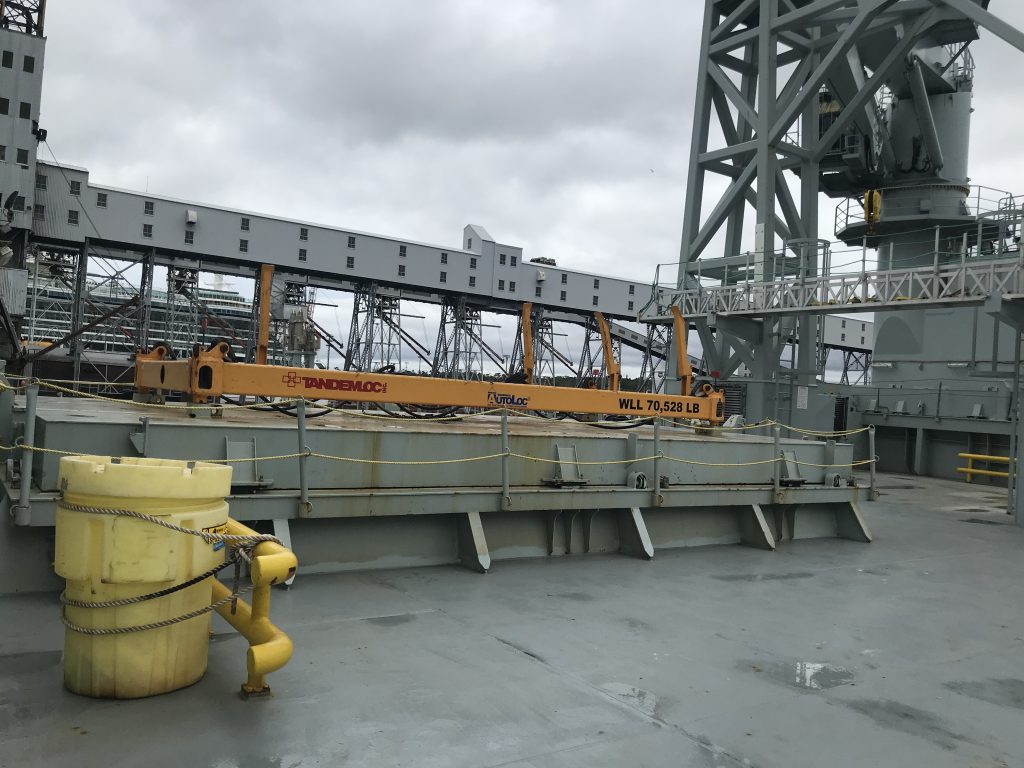
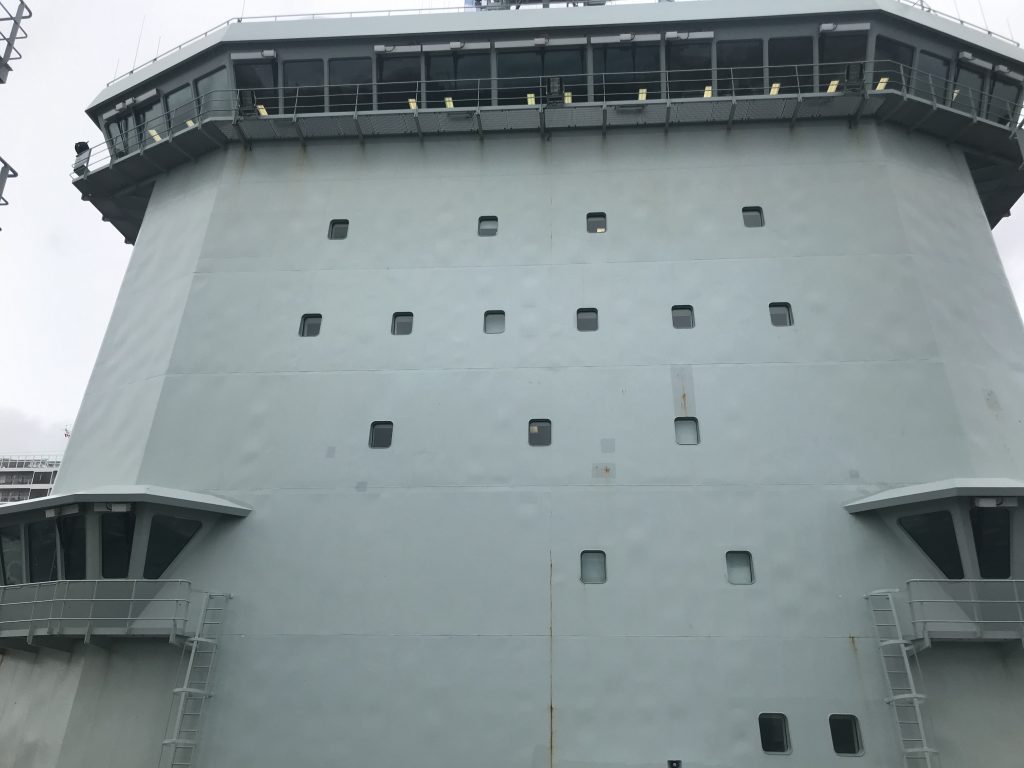
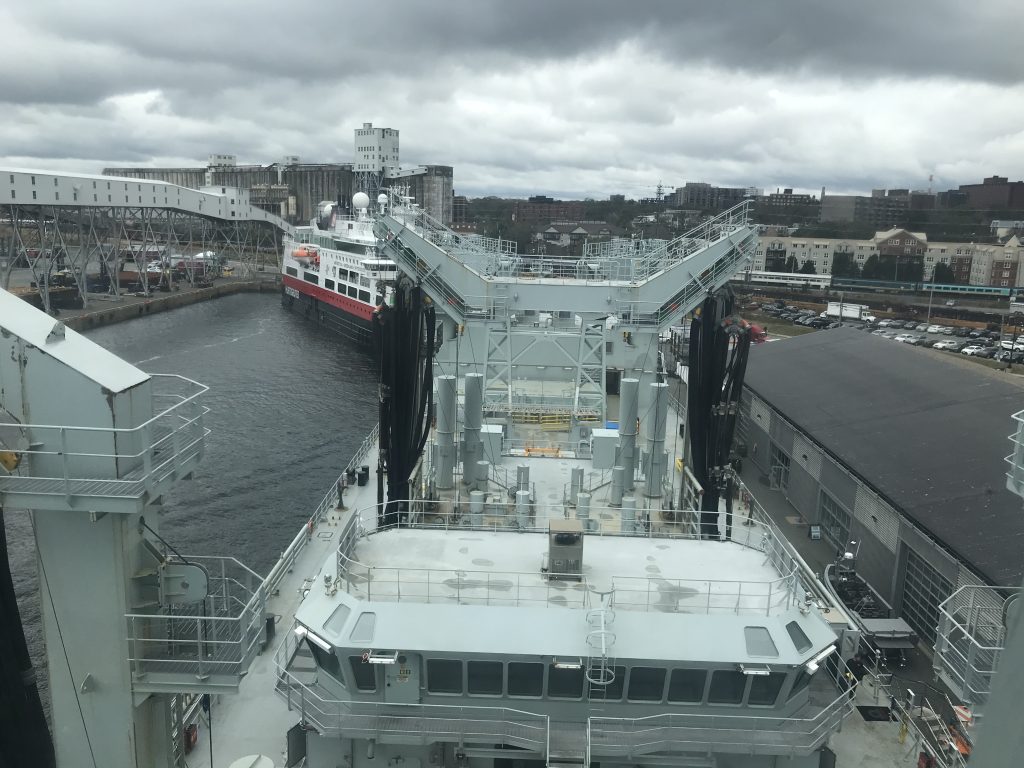
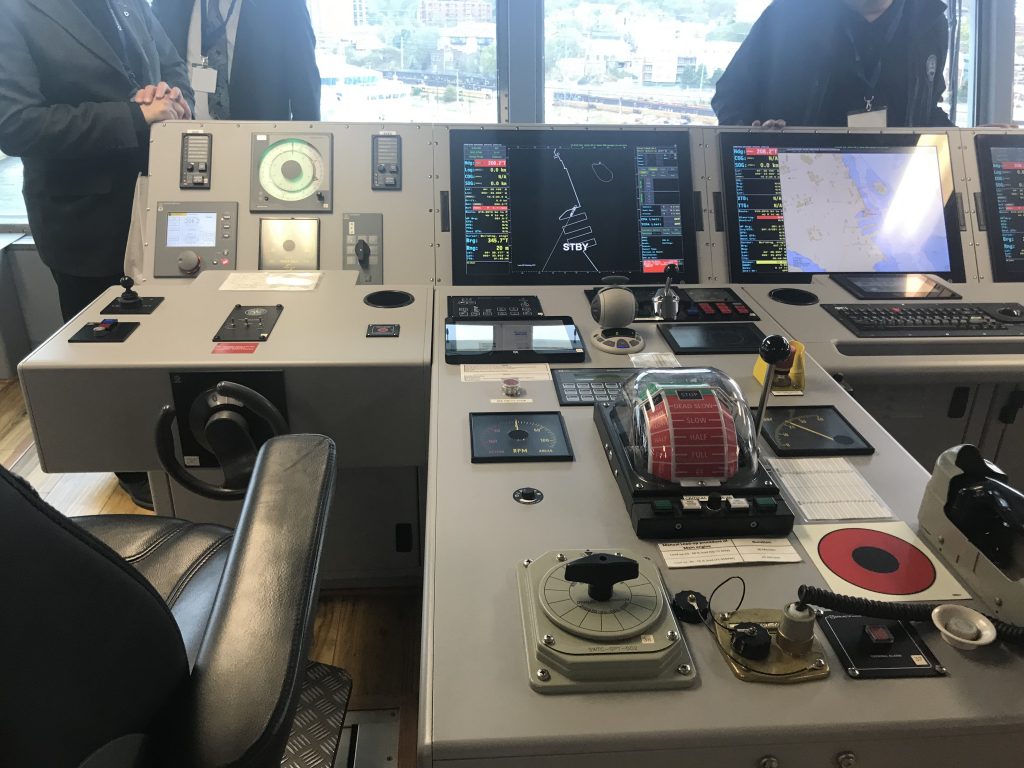
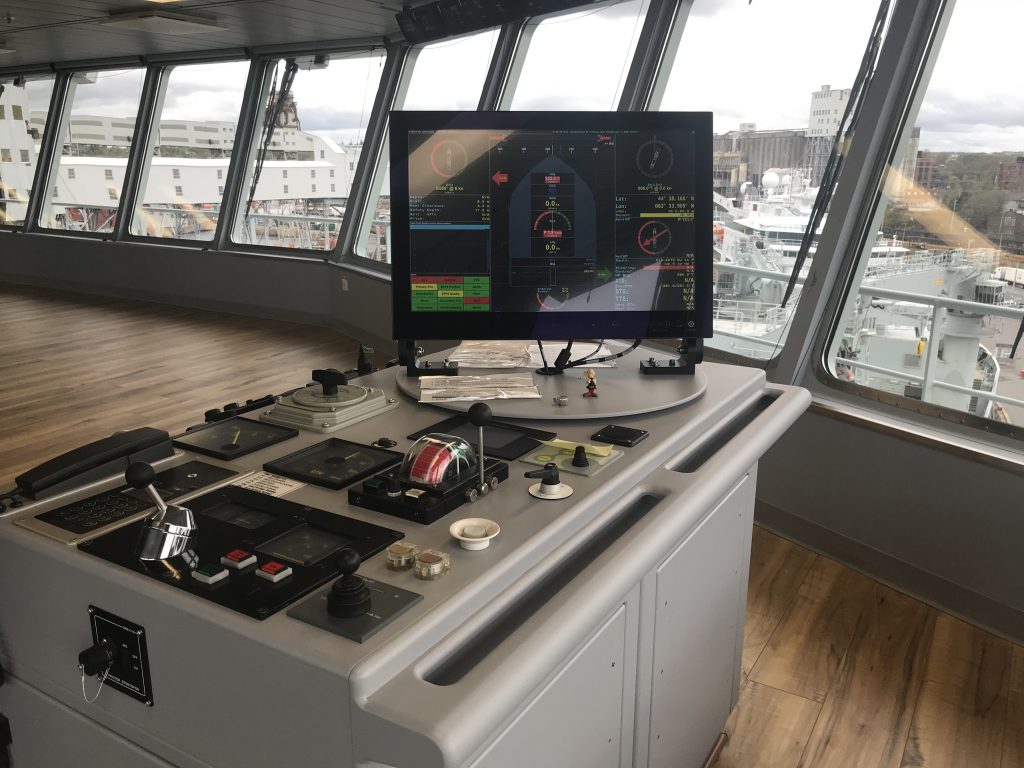
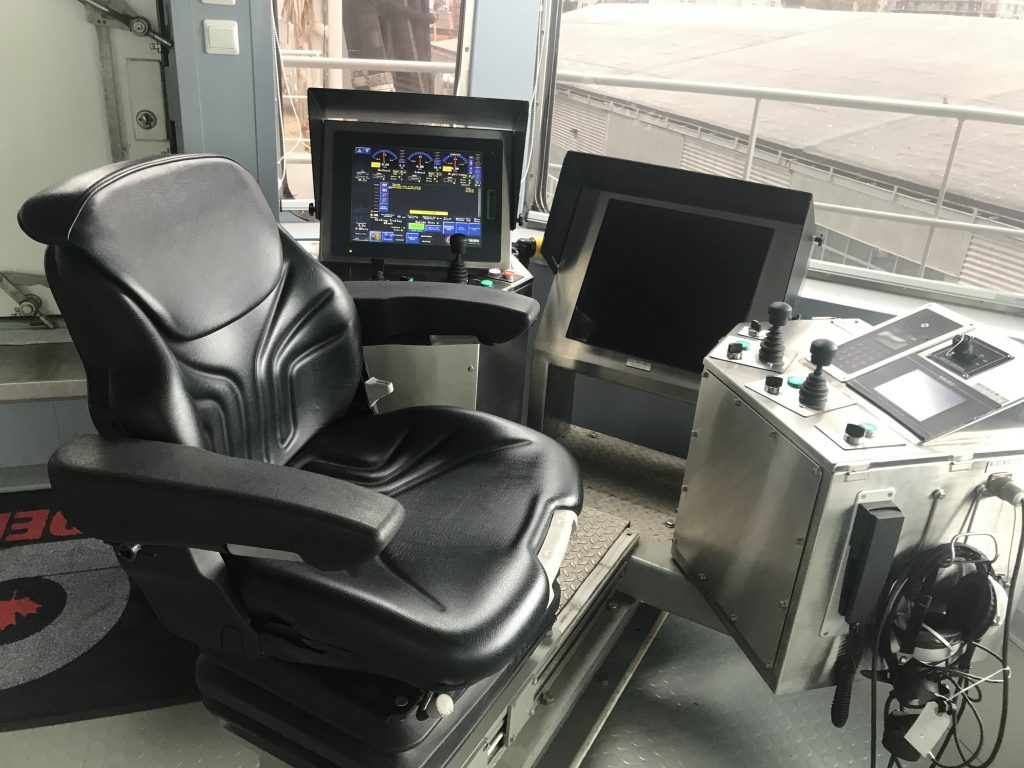





















As part of Defsec Atlantic, Federal Fleet and Hepburn Engineering, the Toronto based company that supplied the RAS gear were offering tours of the ship at Pier 23.



















Most of the functioning Royal Navy was out of port. What remained was laid up or undergoing work periods.











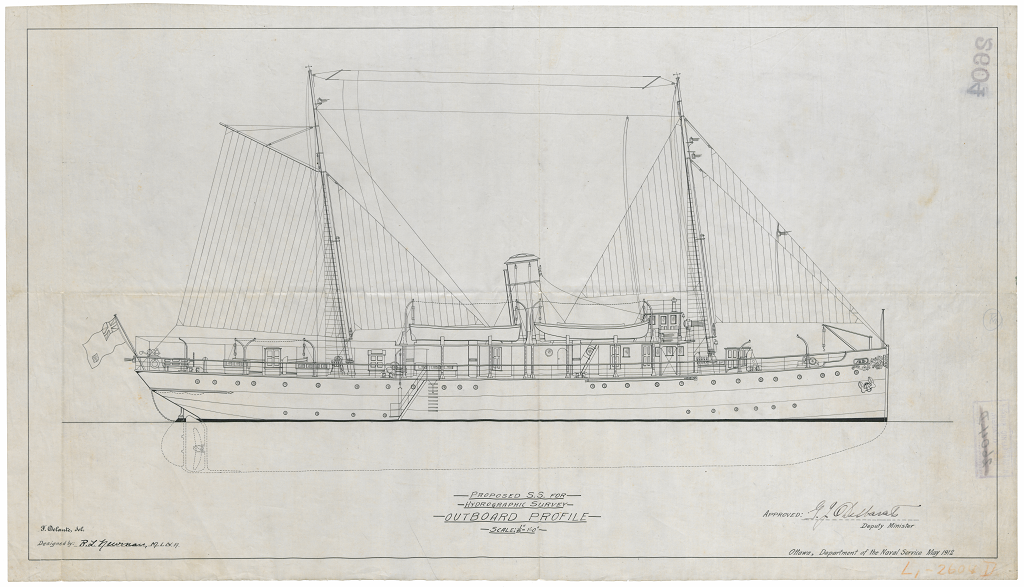
The Province has released the RFP for the Dry docking of the CSS Acadia. the CSS Acadia was built in 1913, and is 106 years old. The much needed work was announced last December.
The Scope of work includes Sandblasting and repainting the hull, Testing and replacement of Steel less then 1.4″ thick, Replacement of a hatch cover, replacement of a fuel tank, improved access to the engine room, and some restoration and maintenance work.
the ship is to be towed to a shipyard, and when returned, will be docked bow in.
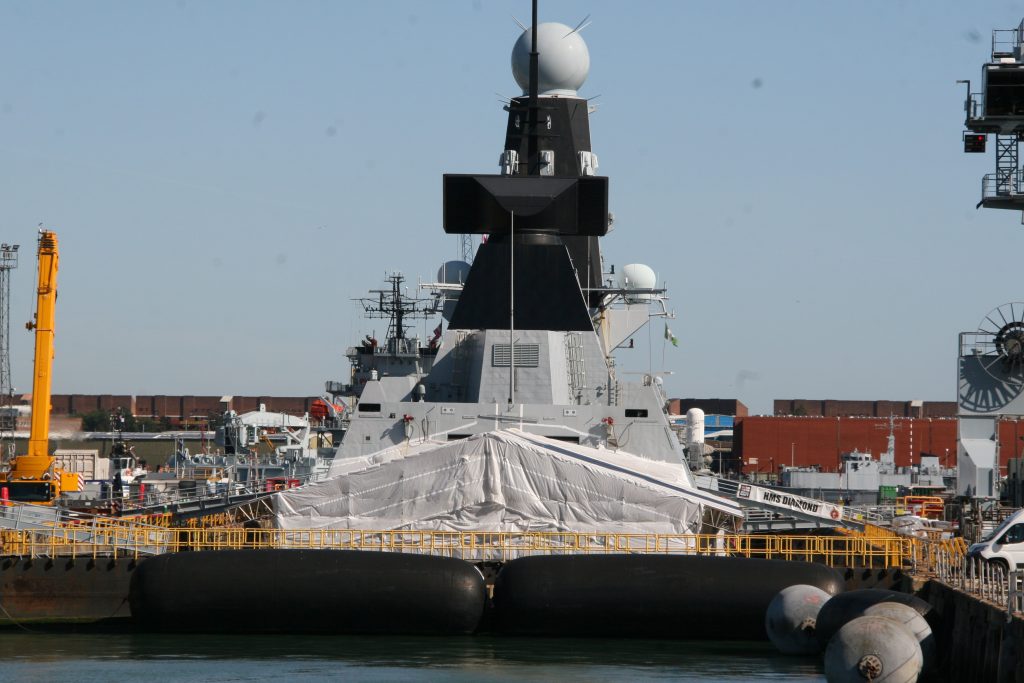
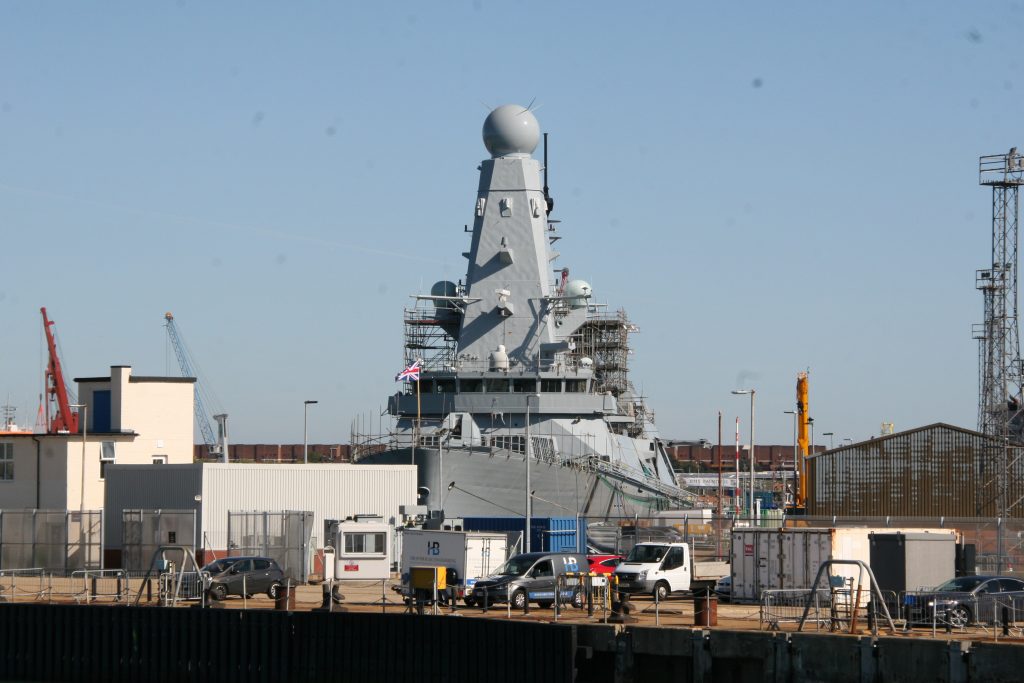
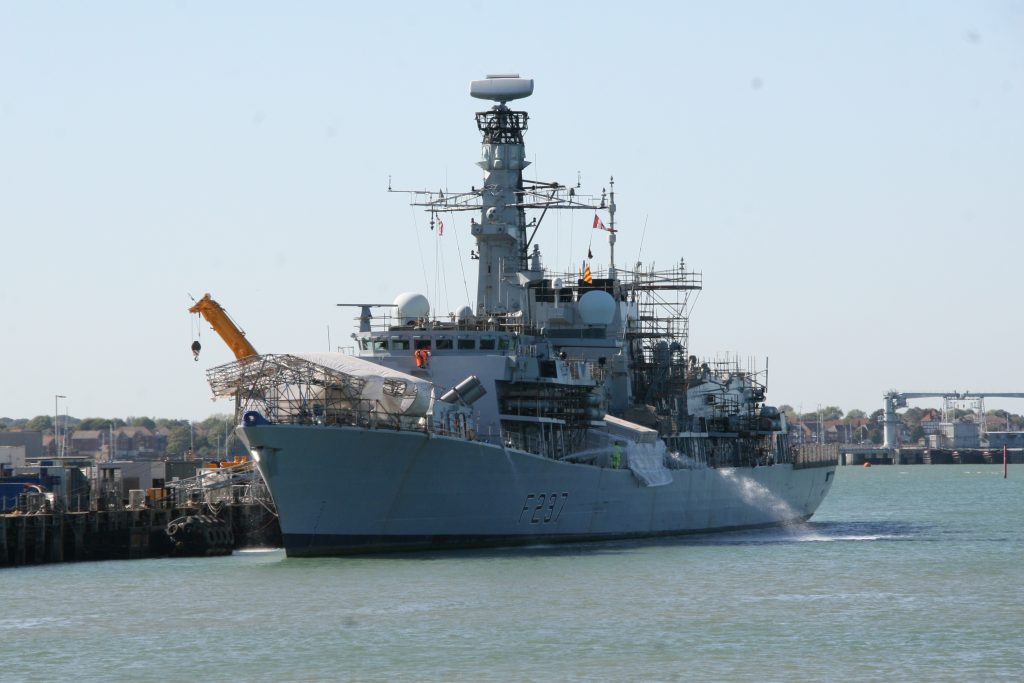
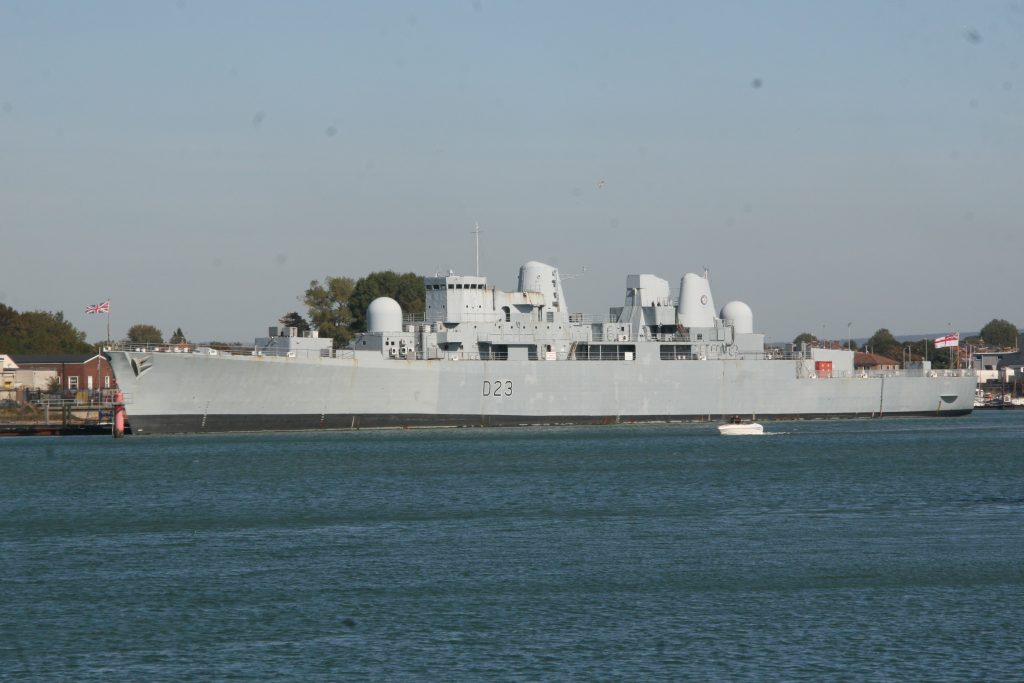
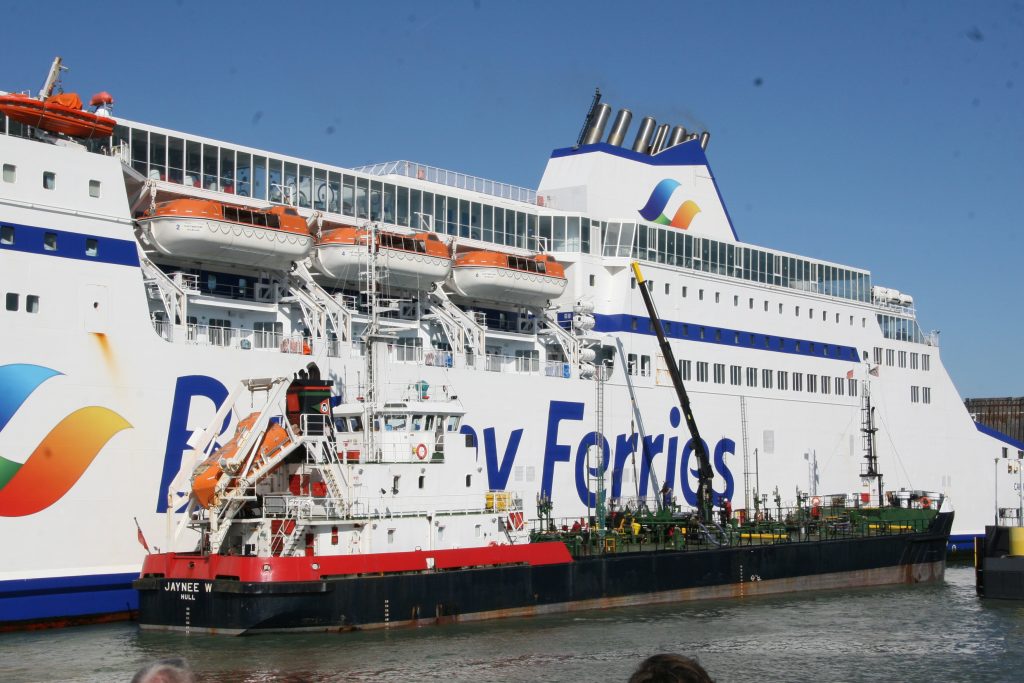
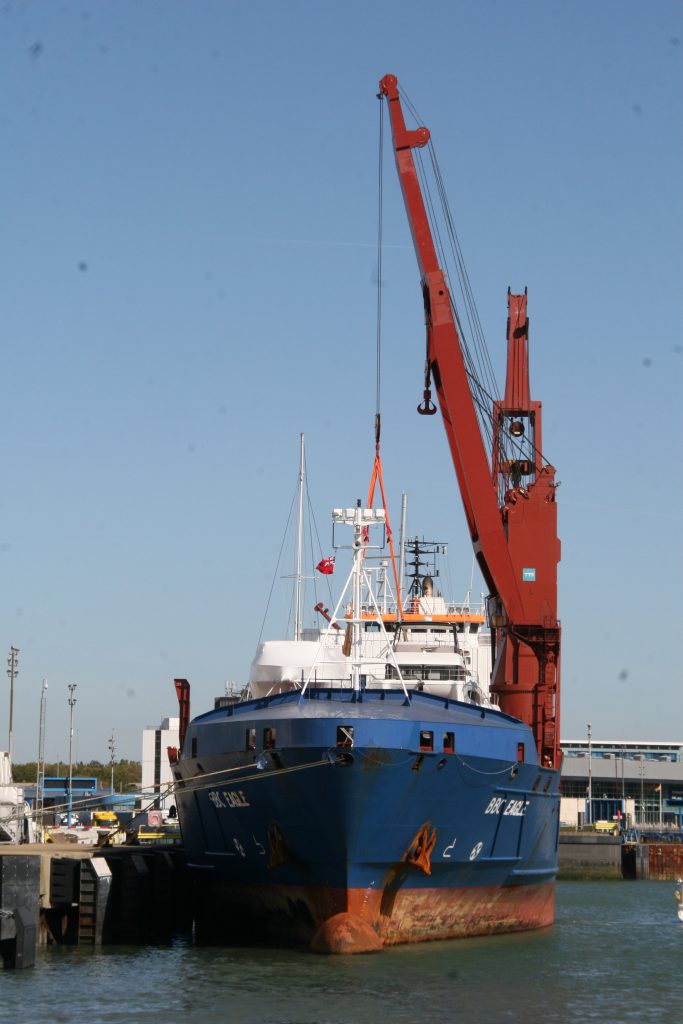
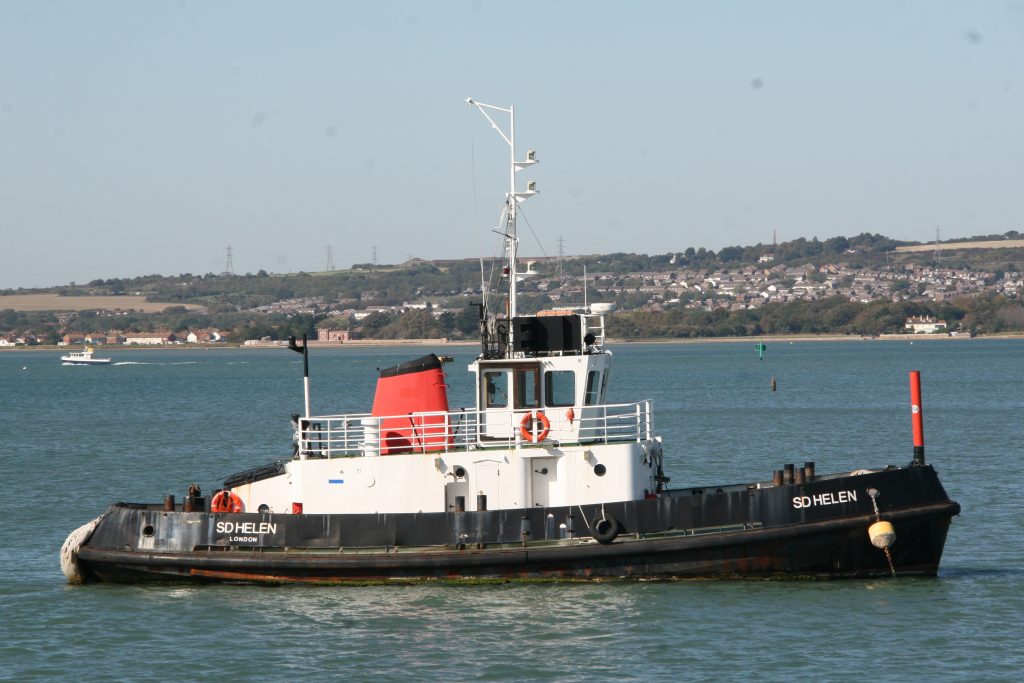
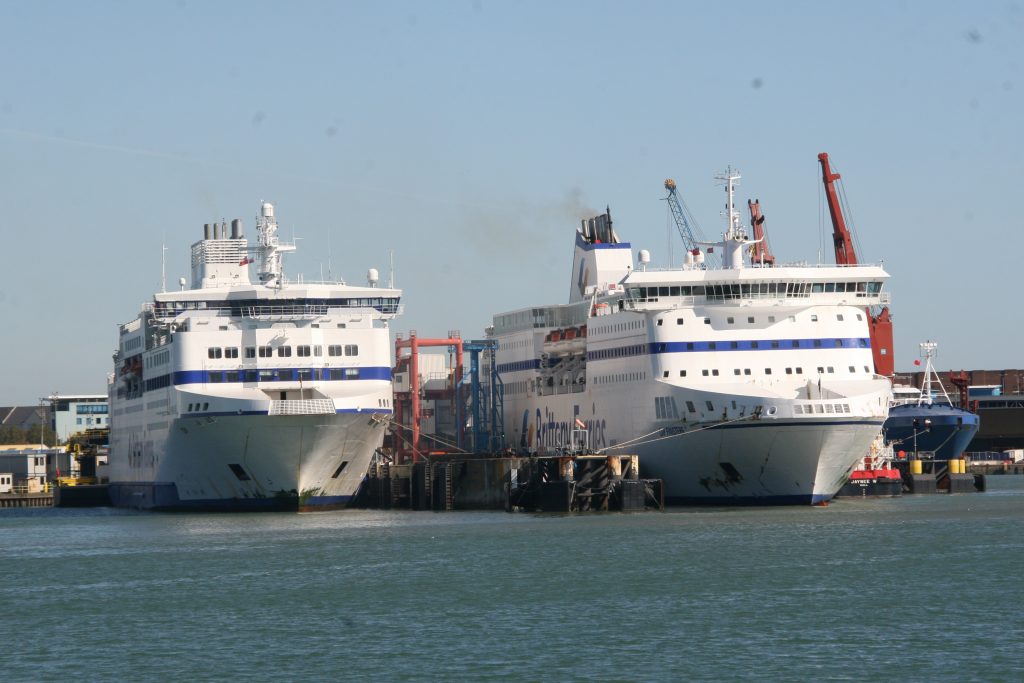
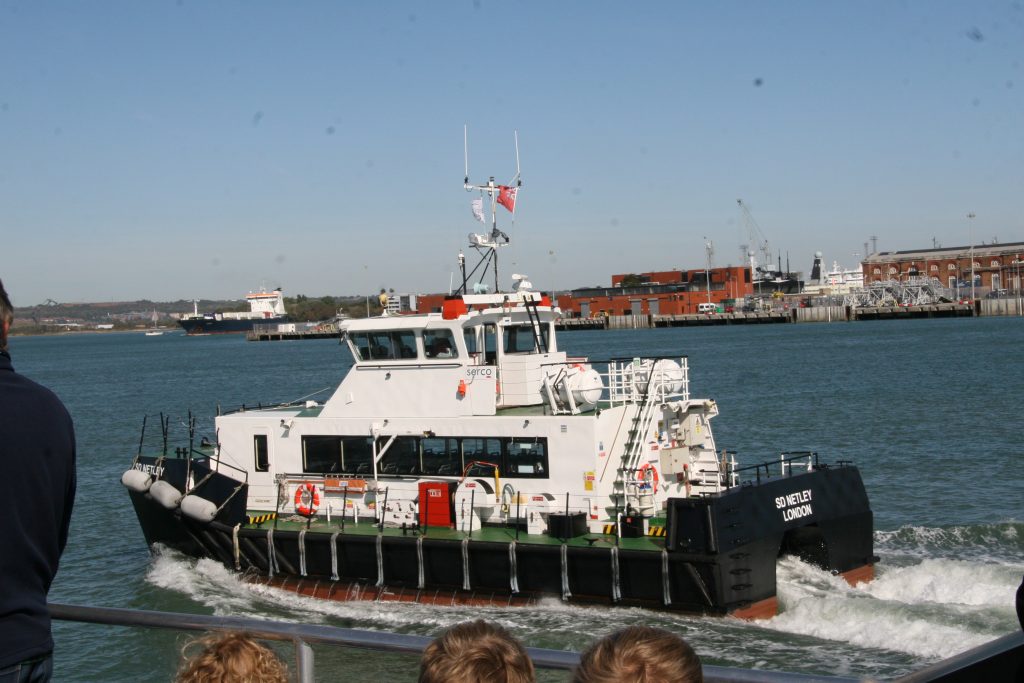
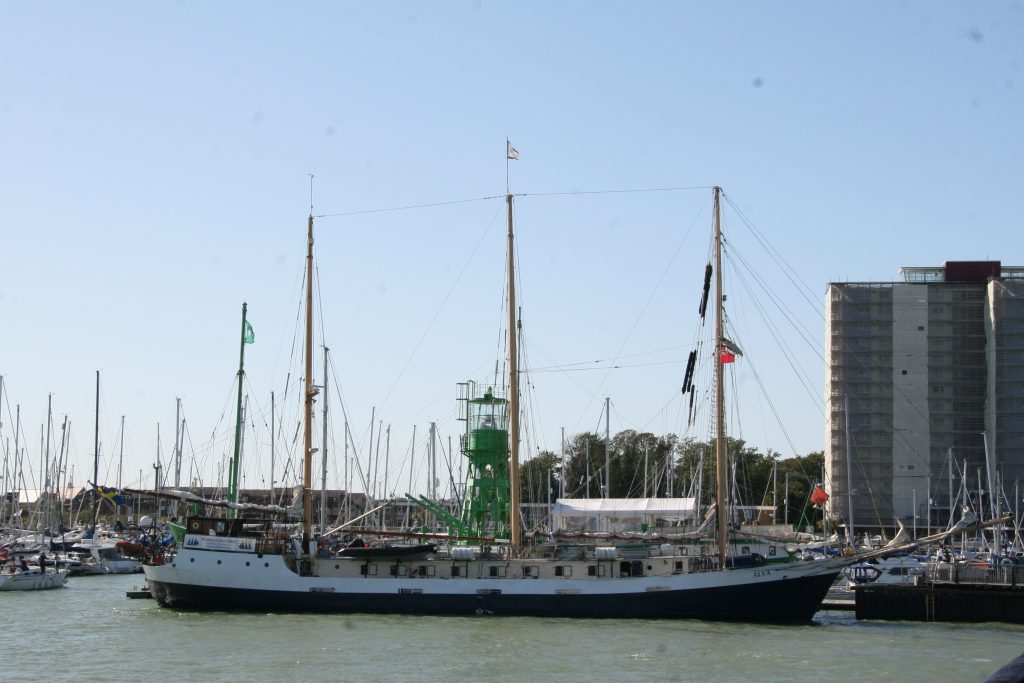
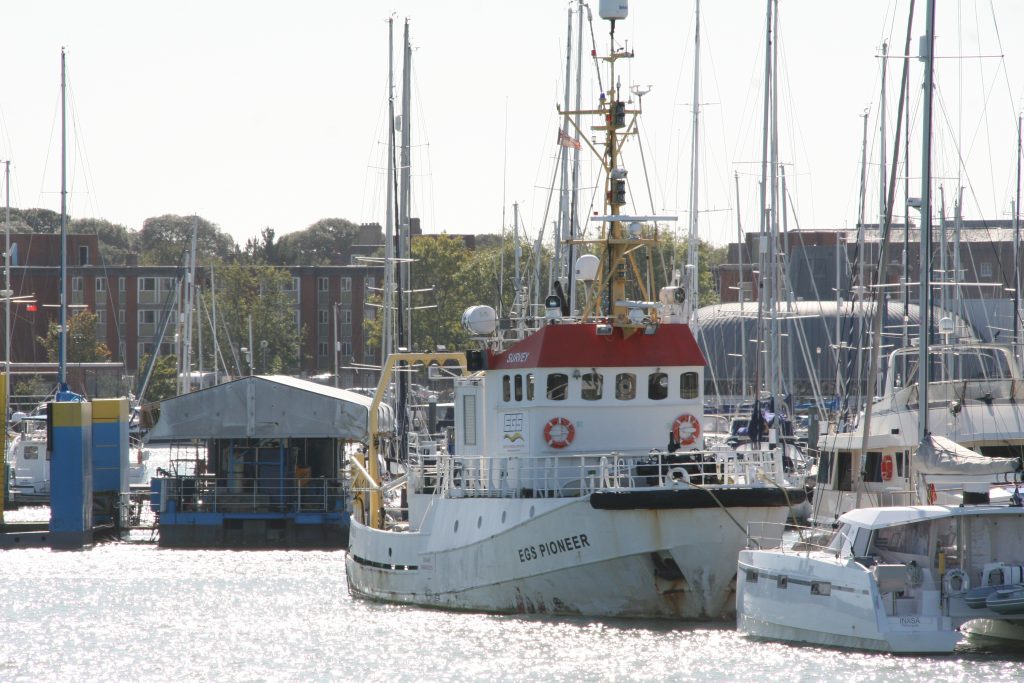
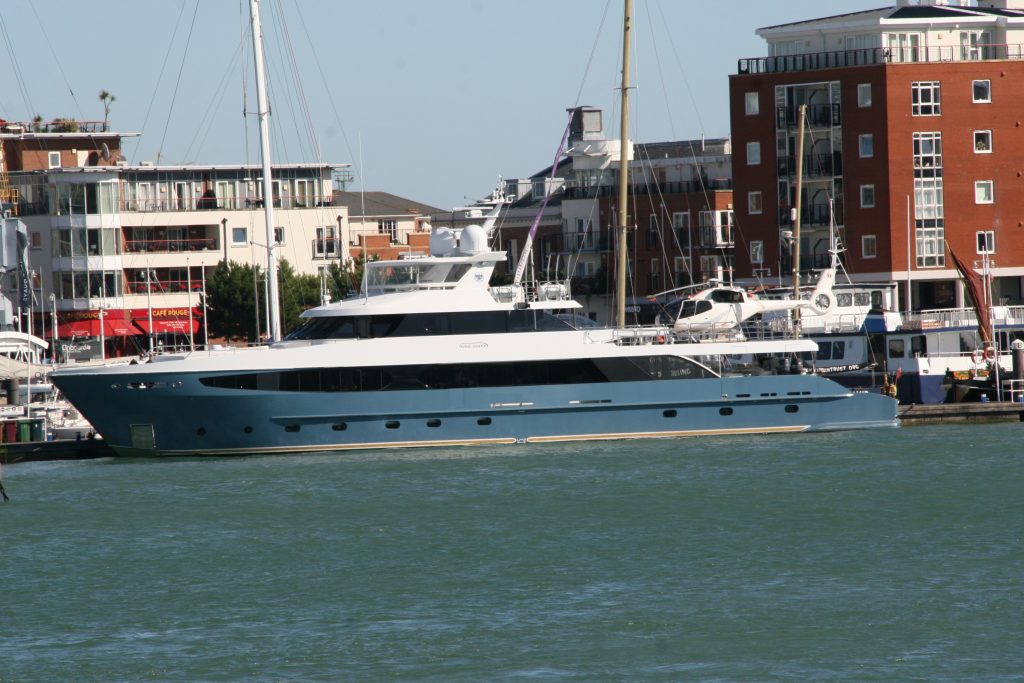
Some recent additions to our ship tours collections, courtesy of our UK Trip. More Can be found at https://www.flickr.com/photos/hfxshippingnews/collections/72157633267966243/
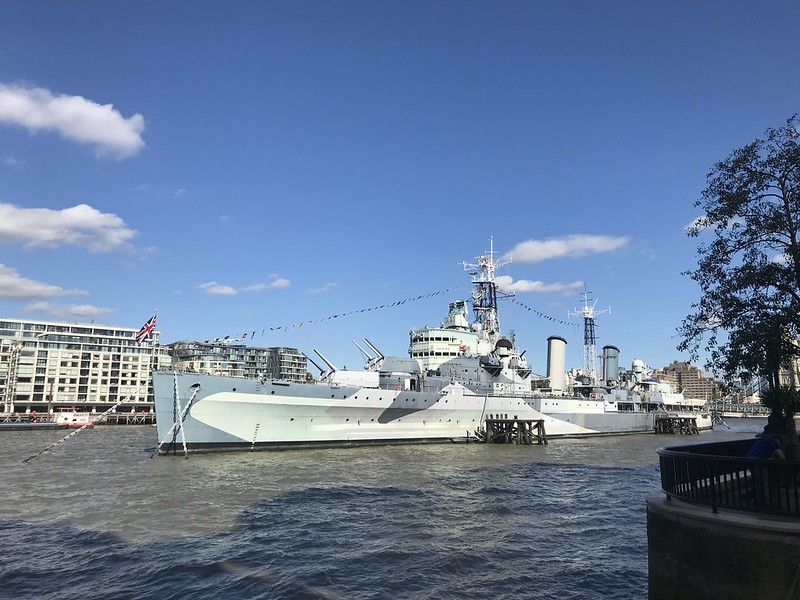

HMS Belfast is a Town-class light cruiser that was built for the Royal Navy in 1939. She severed until 1961, and became a museum ship in the 70’s.
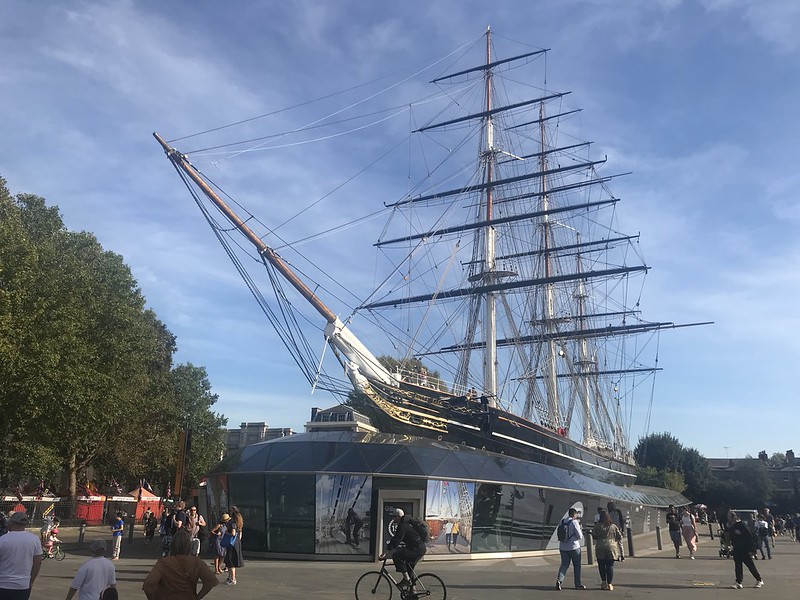

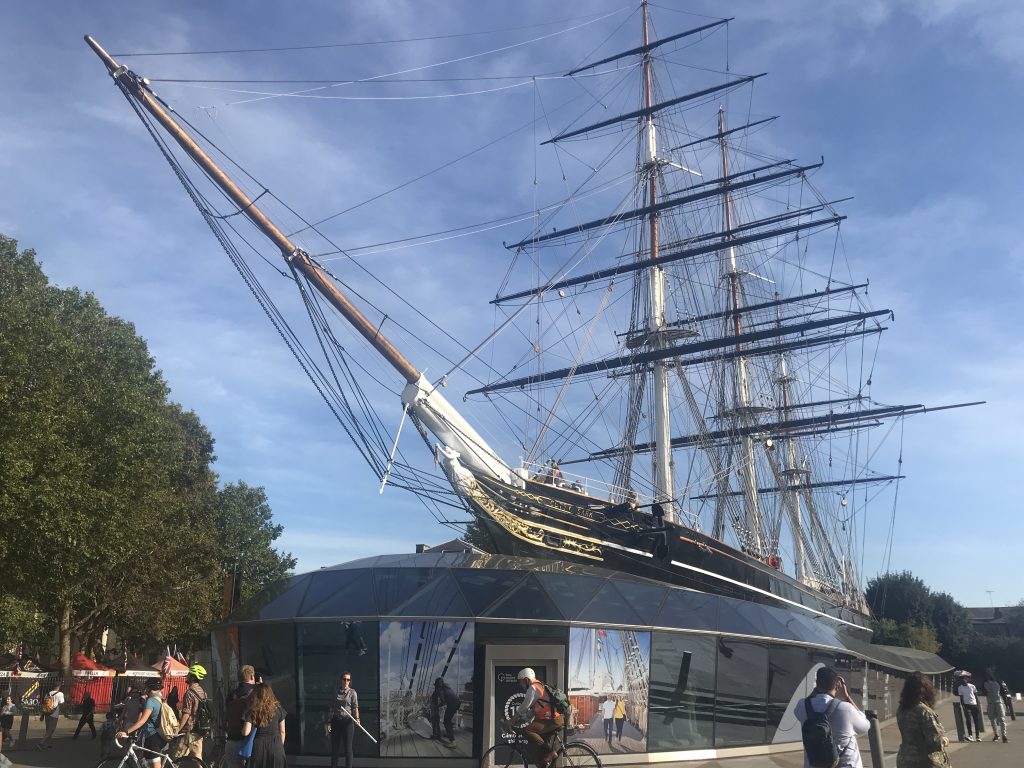
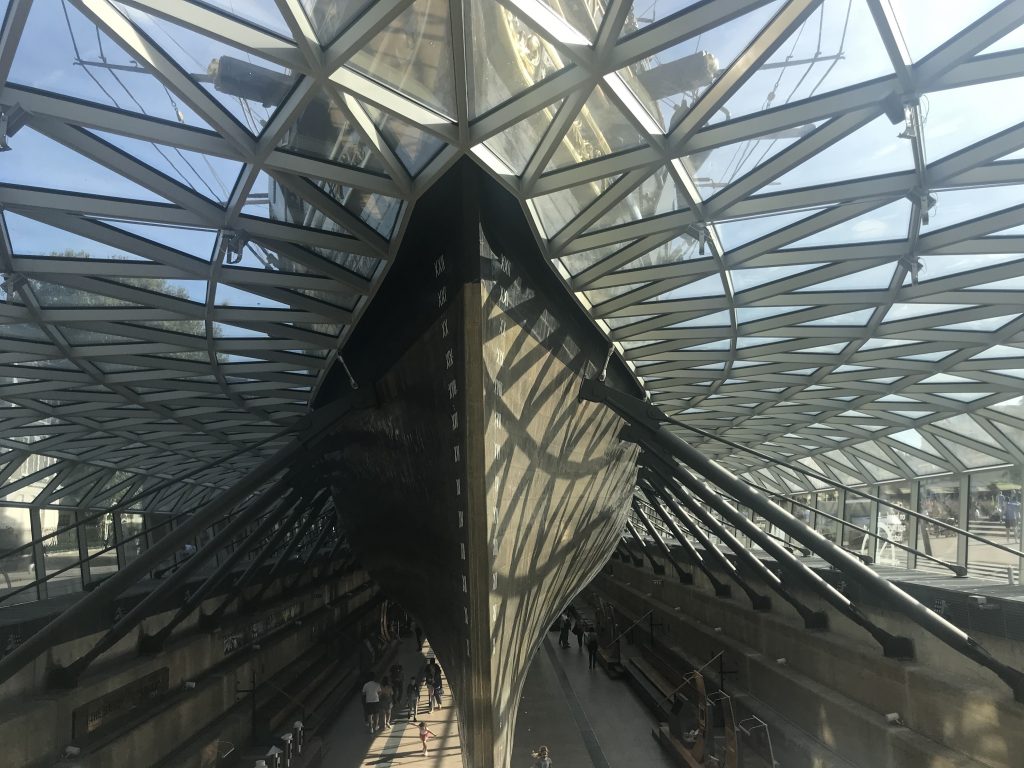
Cutty Sark was built in 1869 for the Jock Willis Shipping Line, she was one of the last and fastest tea clippers to be built. with the Suez open in 1869, steam ships had an advantage, but she contained sailing in the wool trade, before becoming a sail training vessel.
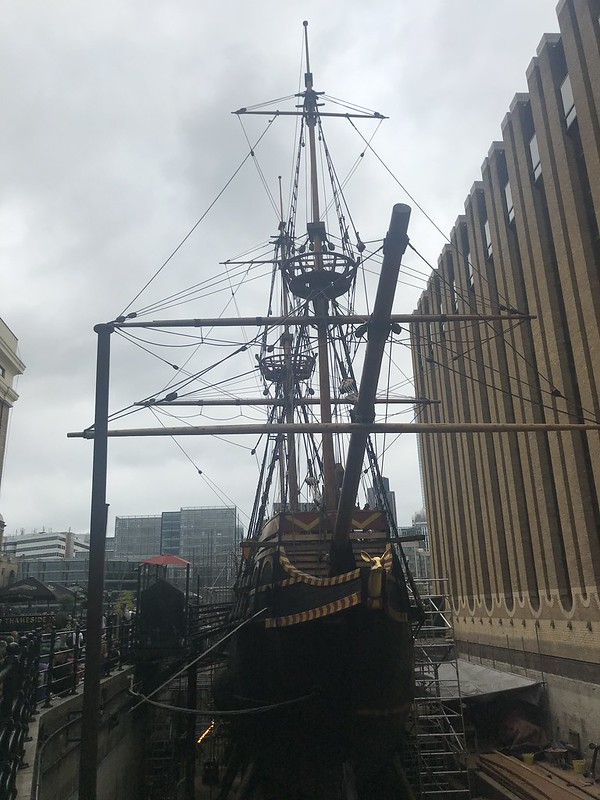

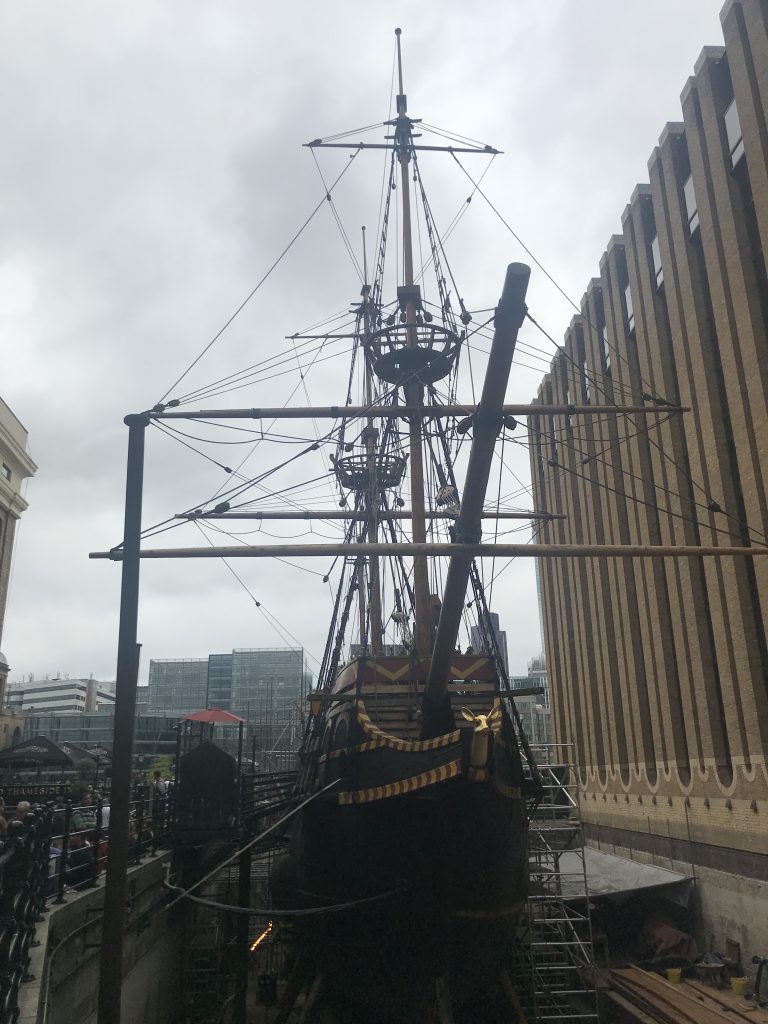
Golden Hind is a replica of Francis Drakes ship that circumnavigated the world between 1577-1580. the replica was built in 1972, and can be sailed.
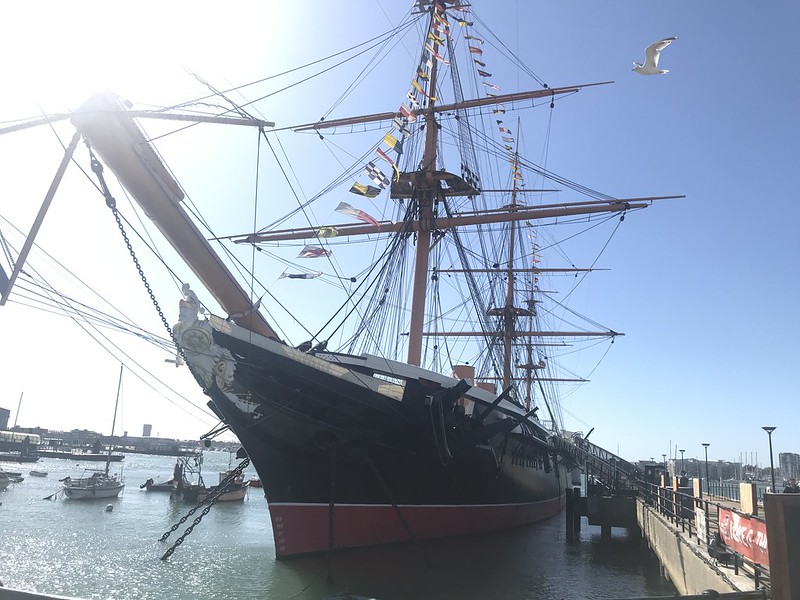

HMS Warrior from 1860 is a 40 gun frigate. Notable as the first RN armour-plated, iron-hulled warship, she also has a steam engine. from 1904 she served as a shore establishment, working as an oiler from 1927-1979.
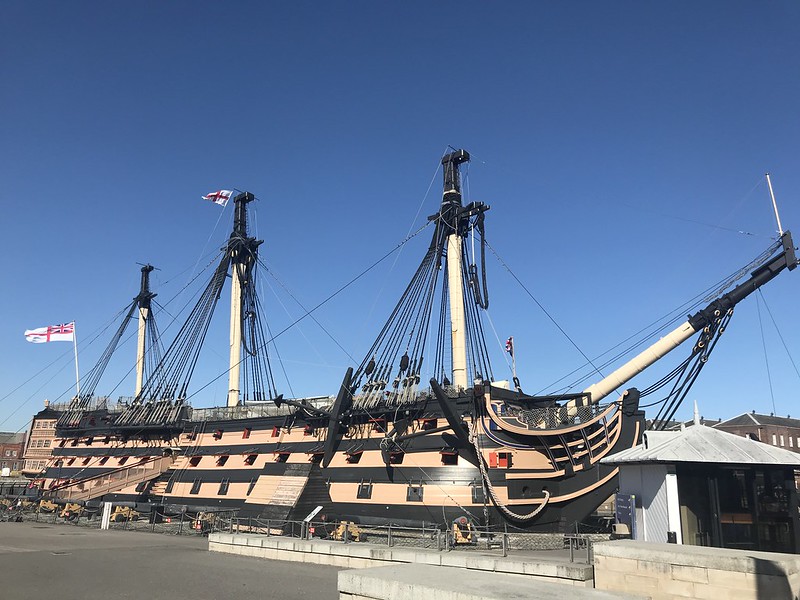

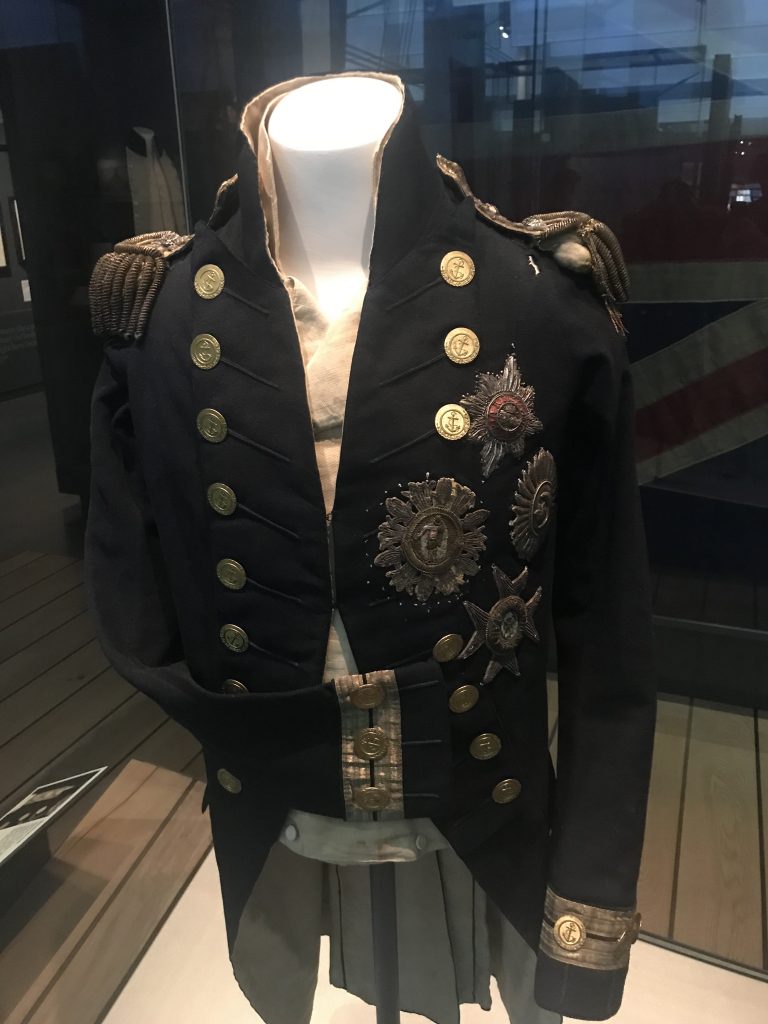
HMS Victory was Nelsons flagship at Trafalgar.
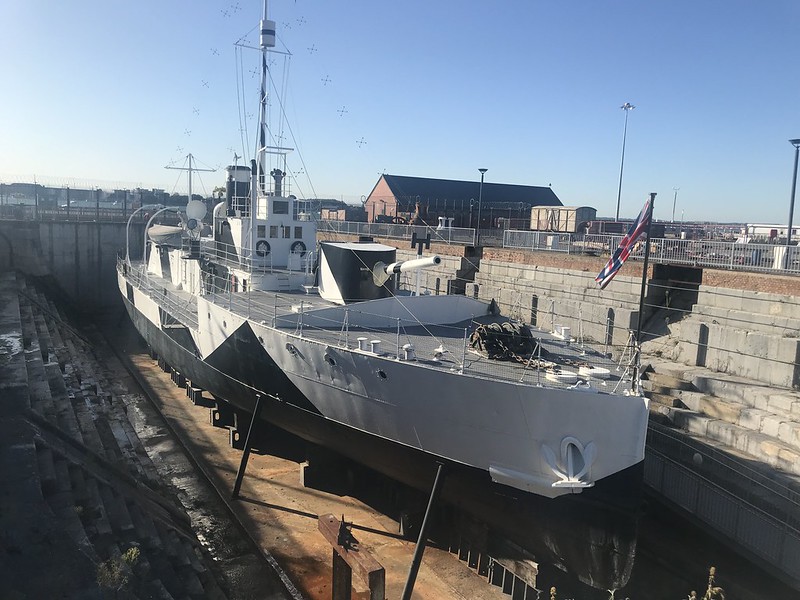

HMS M33 is an M29-class monitor of the Royal Navy built in 1915. She saw active service in the Mediterranean during the First World War, and then served in other rolls until being sold in the as an attraction in 80’s.
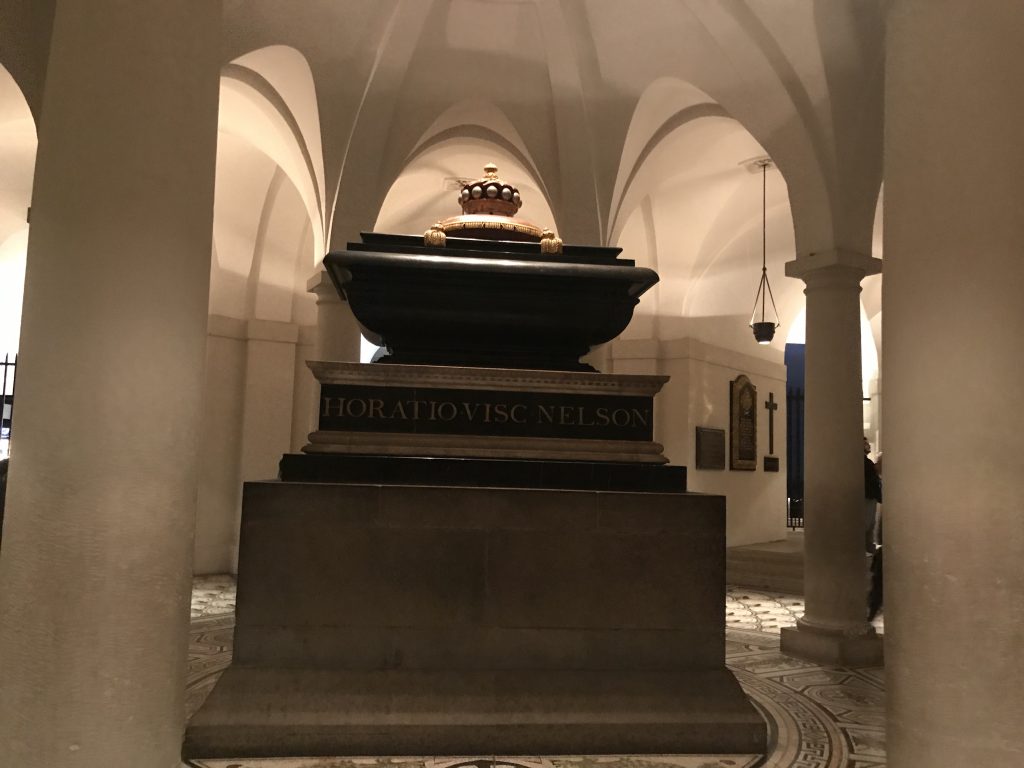
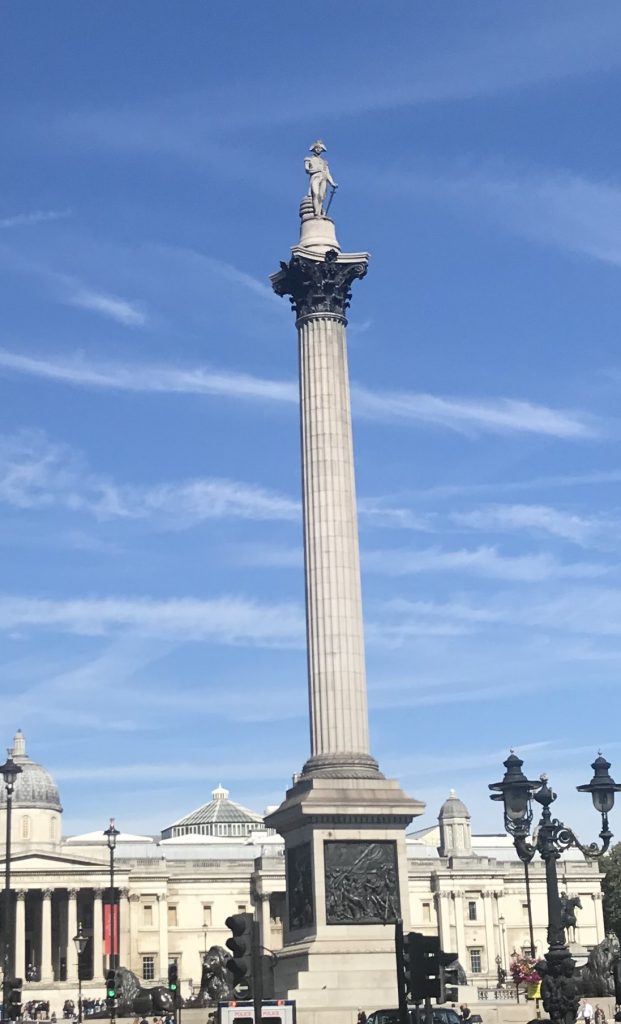
Today is Horatio Nelsons Birthday. So its fitting that today is the day I post some Nelson related stuff from my recent trip, including my visit to HMS Victory.

Above is a gallery of photos of the victory.

















Finding out where you are in the world is done by a combination of Latitude and Longitude.
Latitude is your position above and below the equator. this is easy to calculate by measuring your angle to the sun, and doing some math with tables that tell you what angle you should get depending on the time of year.
Longitude, which is how far around the world you are is more problematic. since the world is round, there are 360 degrees of longitude – this means every hour is 15 degrees of longitude. if you Know your local time, and you know the time at 0, you can figure out how far away your are. that catch if figuring out the time at 0.
in 1612, Galileo figured out that the orbits of the moons of Jupiter could be used to keep time – however, the calculations were complex, and required a stable platform for observation. In 1714, the British parliament passed the longitude act. the act offered a large reward to the first person to demonstrate a practical method of finding longitude on a ship. Enter John Harrison.
Harrison was an amateur clock maker, who went on to build 4 ever improving marine chronometers over the span of 40 years. While reliable clocks existed on land – varying temperature, humidity, and motion of a ship made those devices unsuitable.
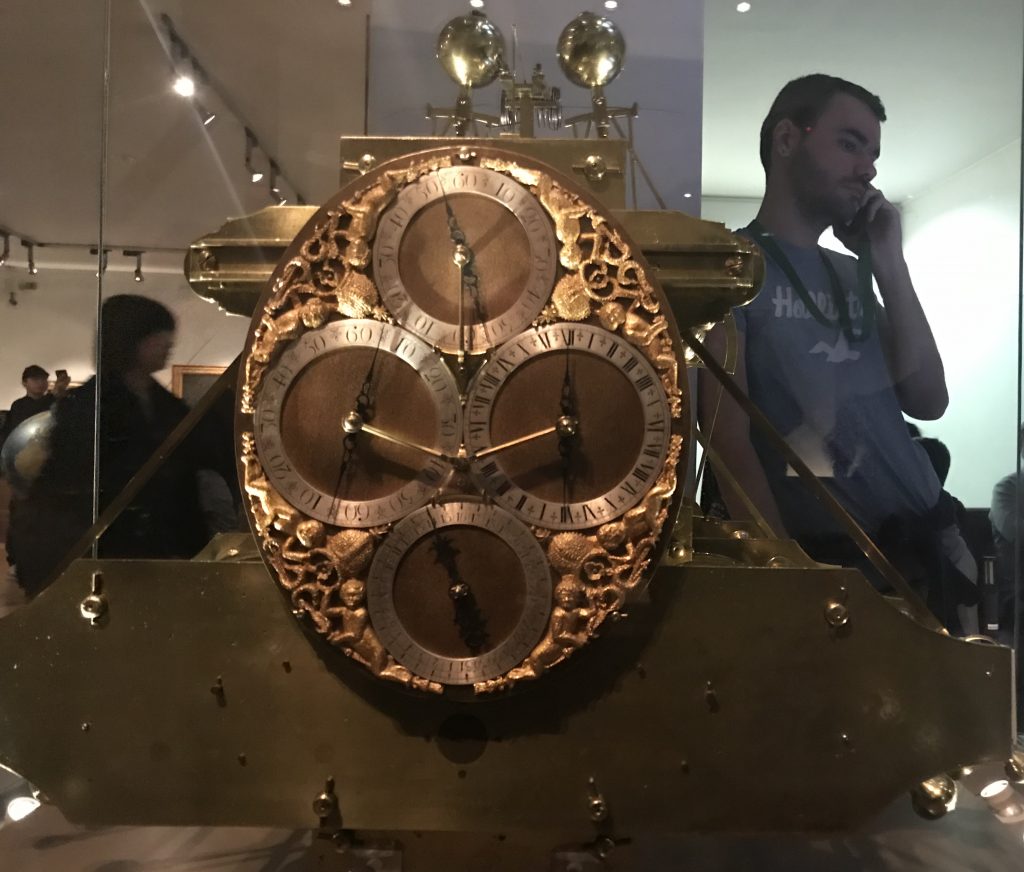

H1 was planed in 1730. Harrison sought funding from Halley (of Halley’s Comet fame) who was the Astronomer royal in Greenwich, but was refereed to George Graham, who agreed to fund it. five years later H1 was completed. the Sea clock worked, and the board of longitude funded its further development.
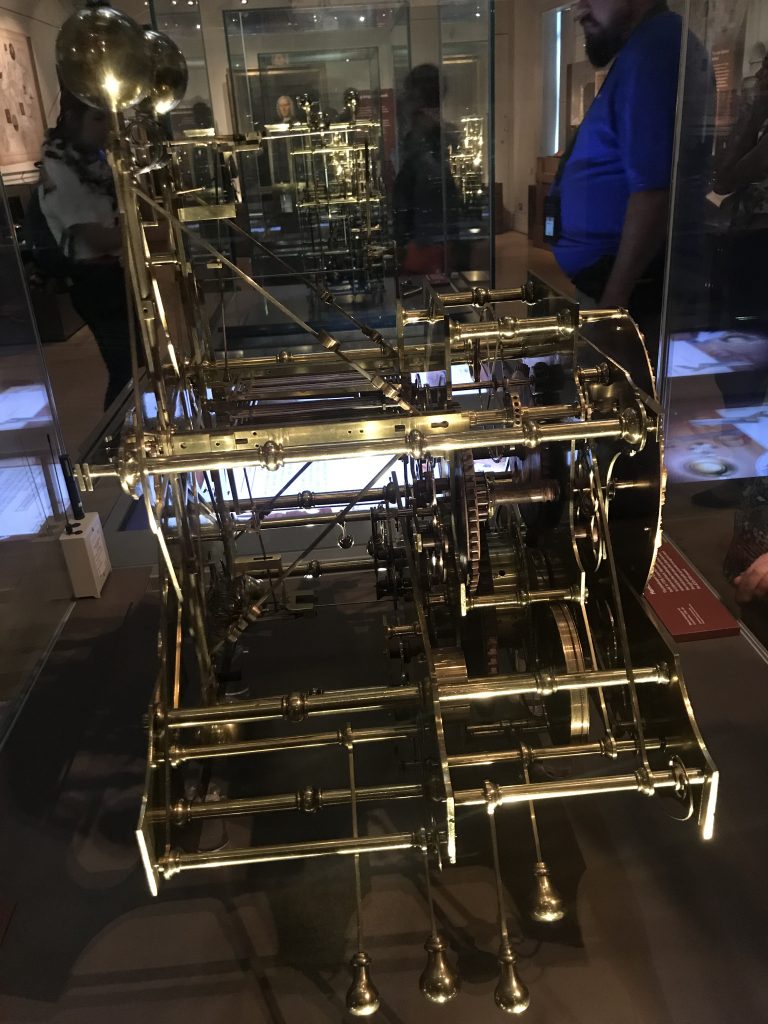
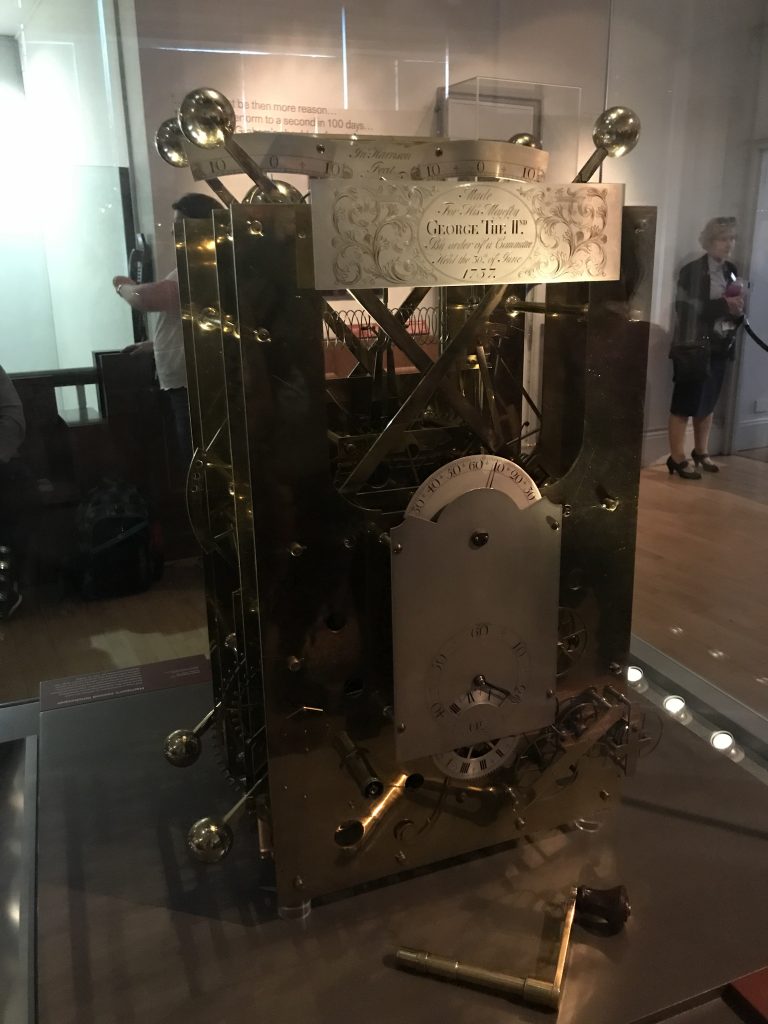
H2 was ready for testing at sea in 1741. With the country at war with Spain, the Chronometer was deemed to risky to put to sea, and Harrison himself discovered an issue with the balances, where they could be affected by the motion of a ship. H2 was abandoned.
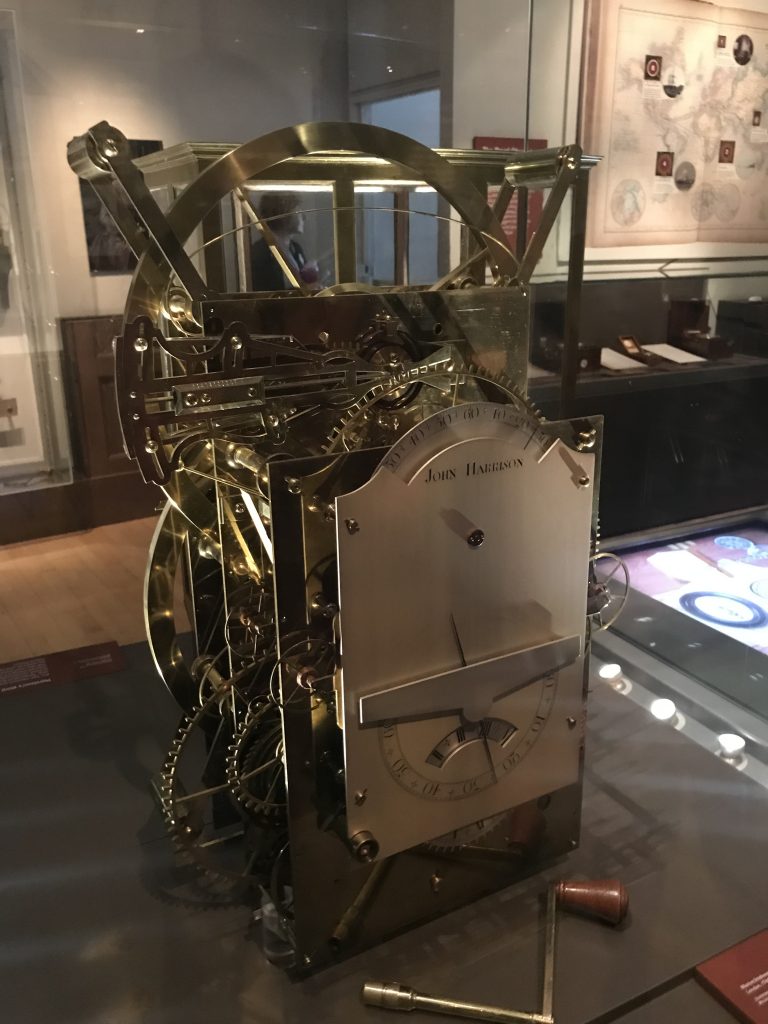


Harrison received further funding from the Longitude board, and produced the H3. H3 replaced the bar balances with circular balances, and took 17 years to develop.
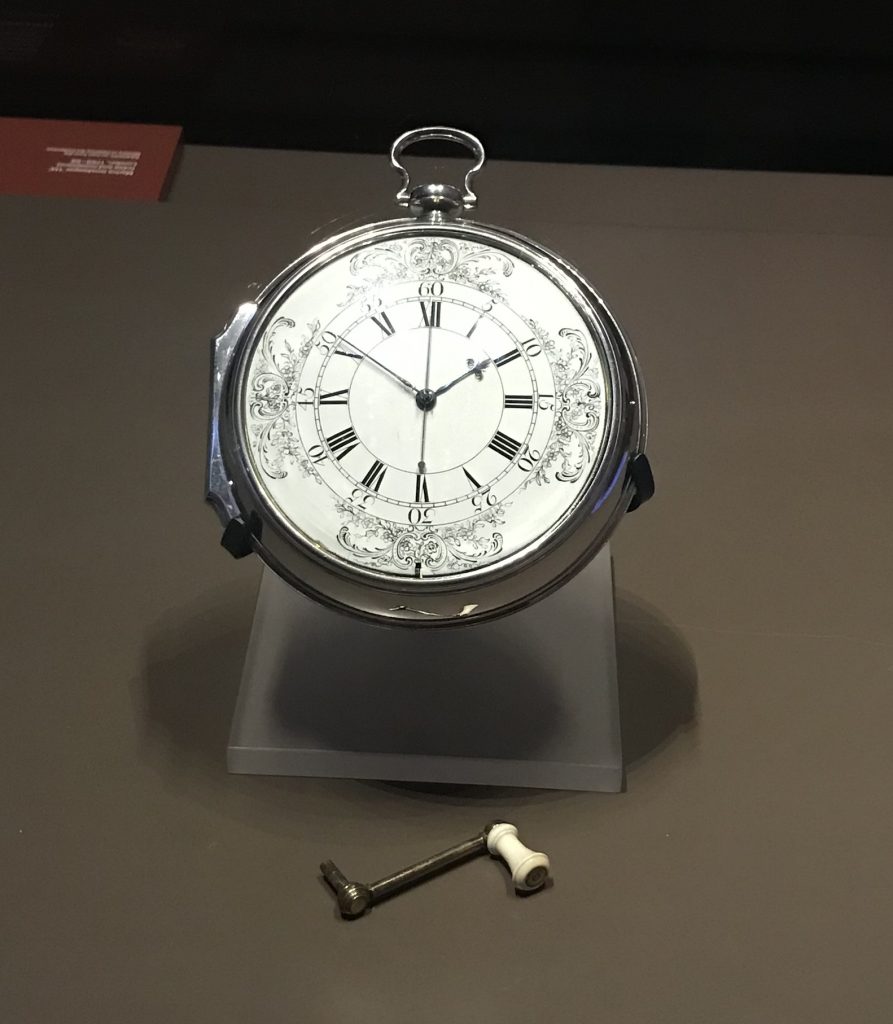

H4 was the the result in a change of thinking on the part of Harrison. he realized that reliable accurate watches existed, and worked to refine and improve them. Sea Watch 1, or H4, took 6 years to build, and is 13cm in diameter. it was trialed on a trip to Kingston Jamaica in 1761, and was found to accurate to one nautical mile after an 81 day voyage.
Harrison turned over the design, and it was duplicated. Cook took the K1, a copy of H4 built by Larcum Kendall on his second and third voyages. K2 was used by Bligh on the bounty, and was kept by the mutineers. it was recovered in 1808.
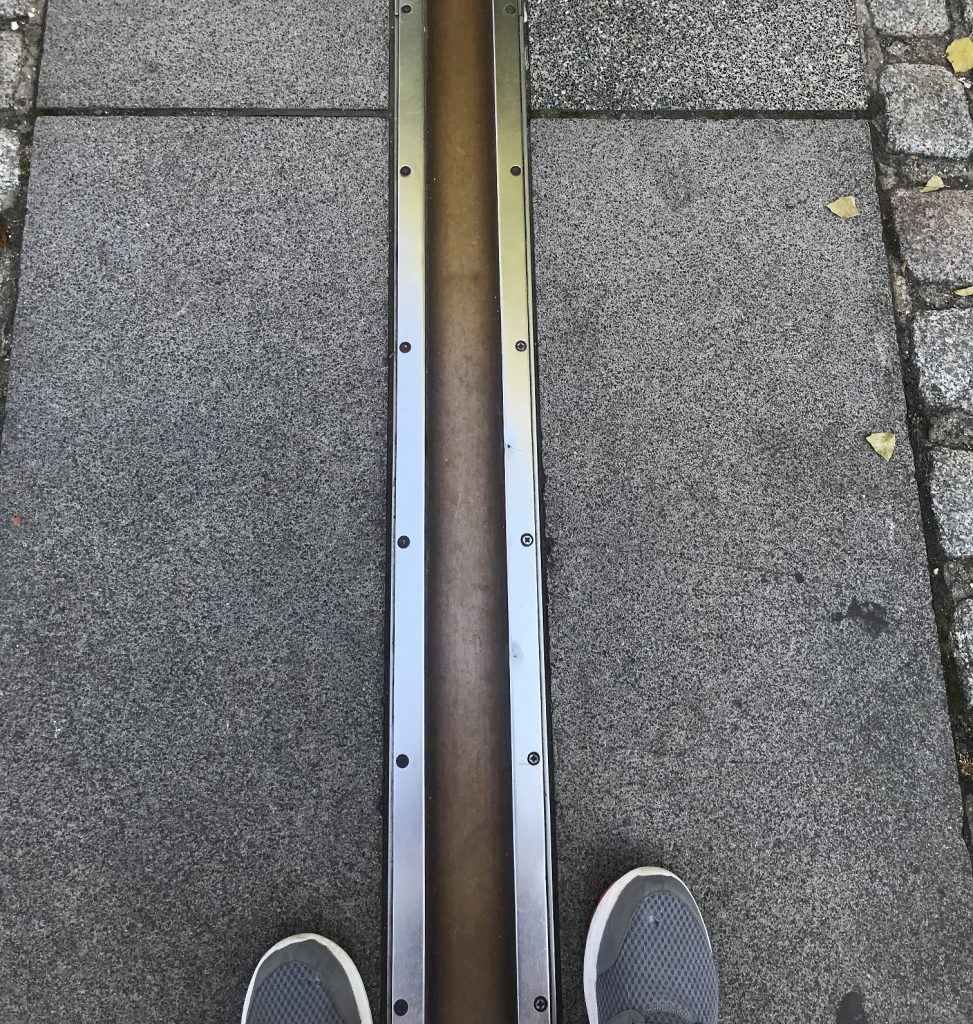

the clocks are housed at the Royal Observatory in Greenwich, Home to the Prime Meridian, 0 degrees Longitude. Its marked on a line on the ground.
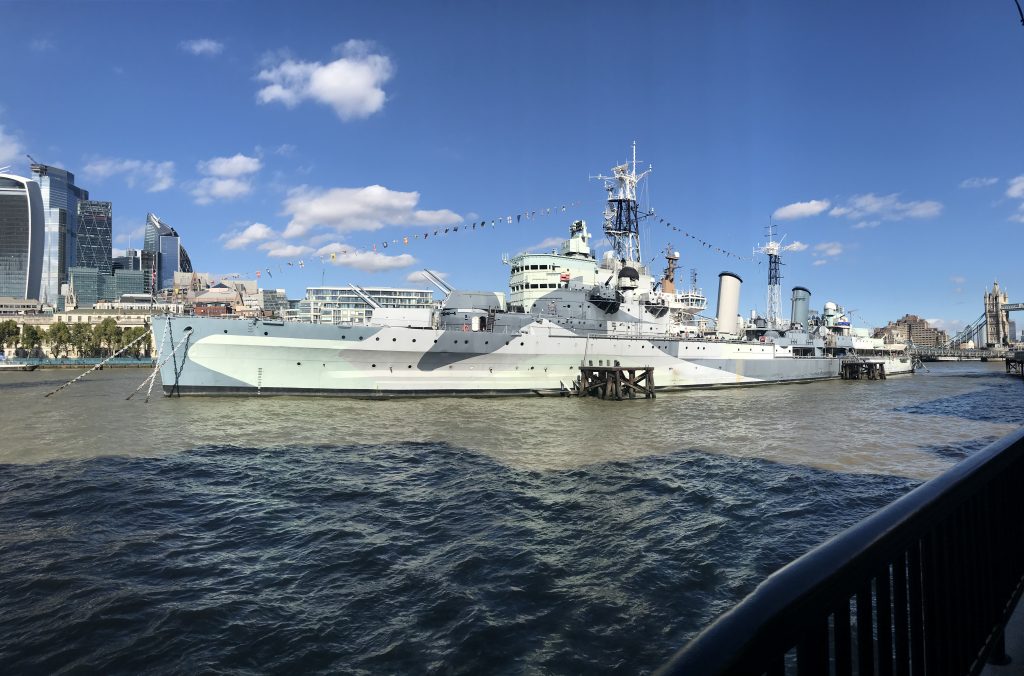

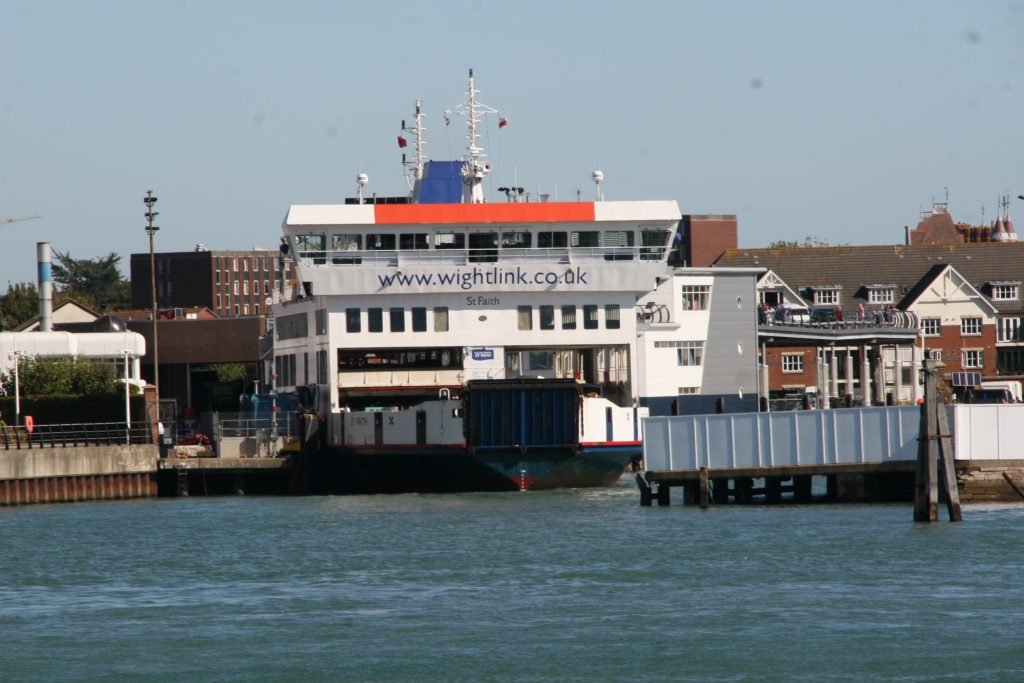
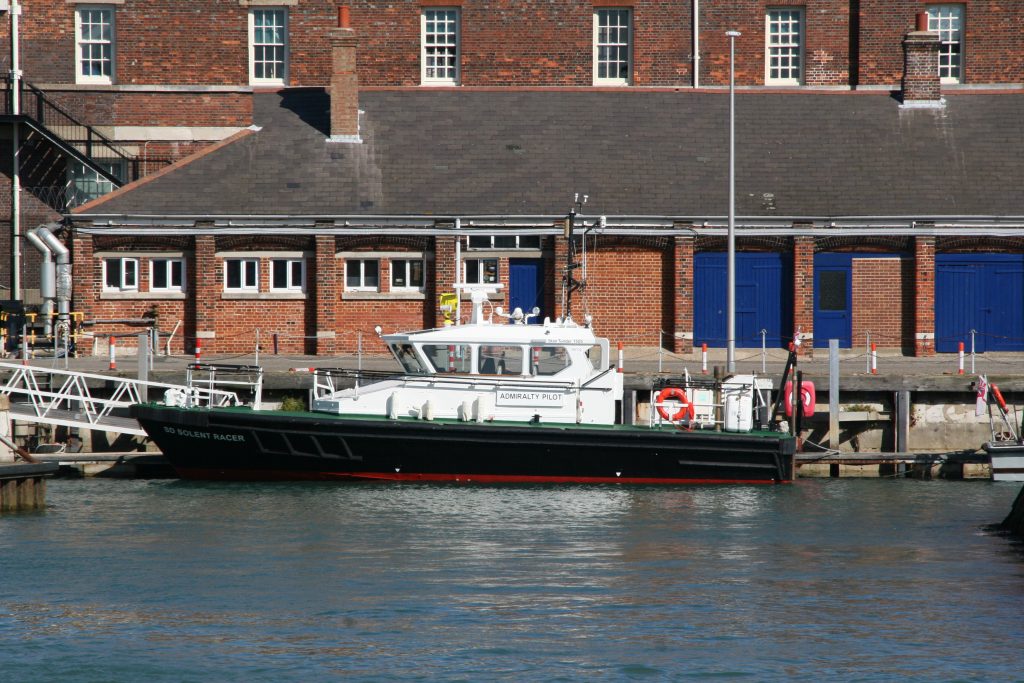
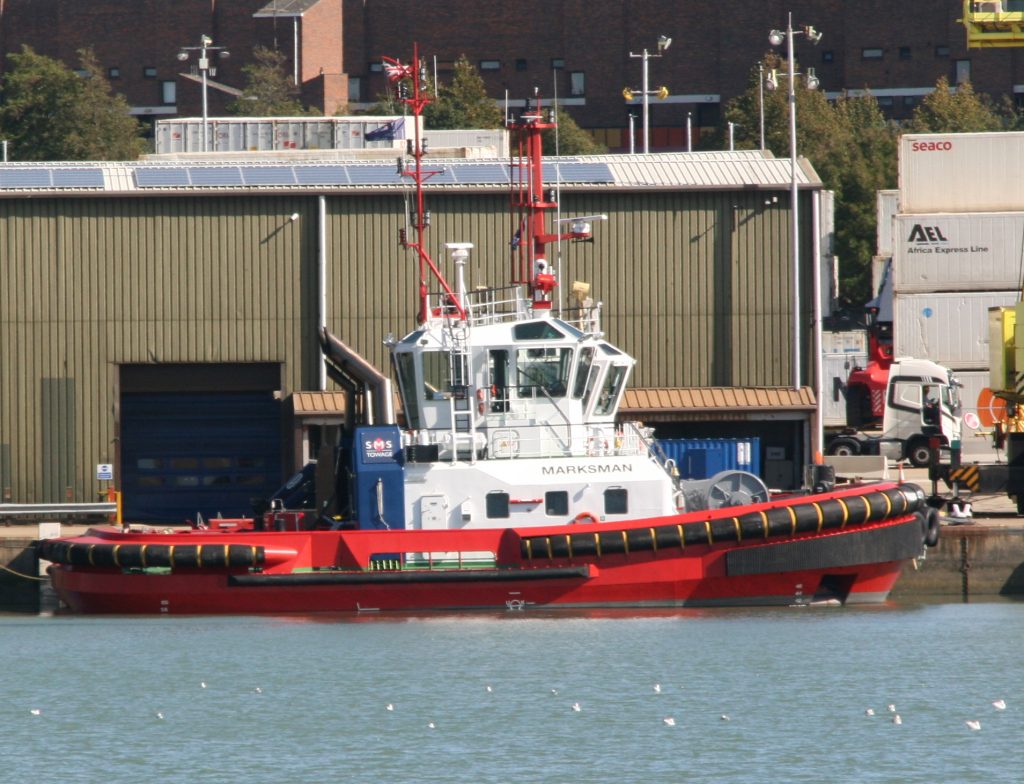
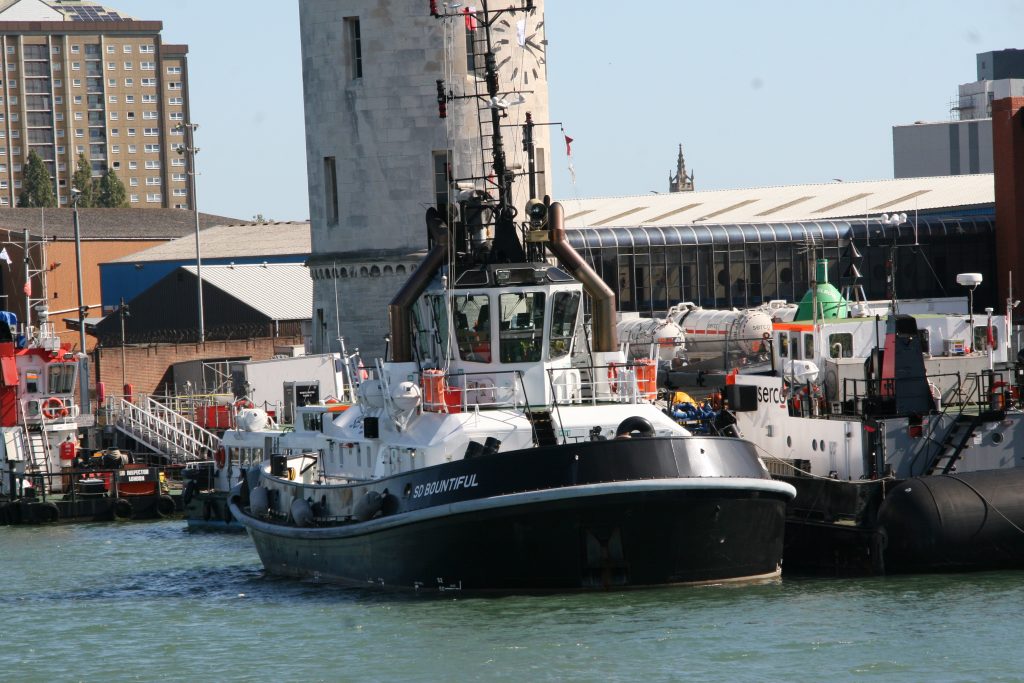
Last week in the Herald, I touched on Preserving our maritime Heritage. London is surrounded by preserved historic ships, As well as the National Maritime museum in Greenwich. More maritime history is preserved at Portsmouth Historic Dockyard, and other sites around Britain.
There will be more posts from the trip in the coming days. including a look at the Historic Dockyard.
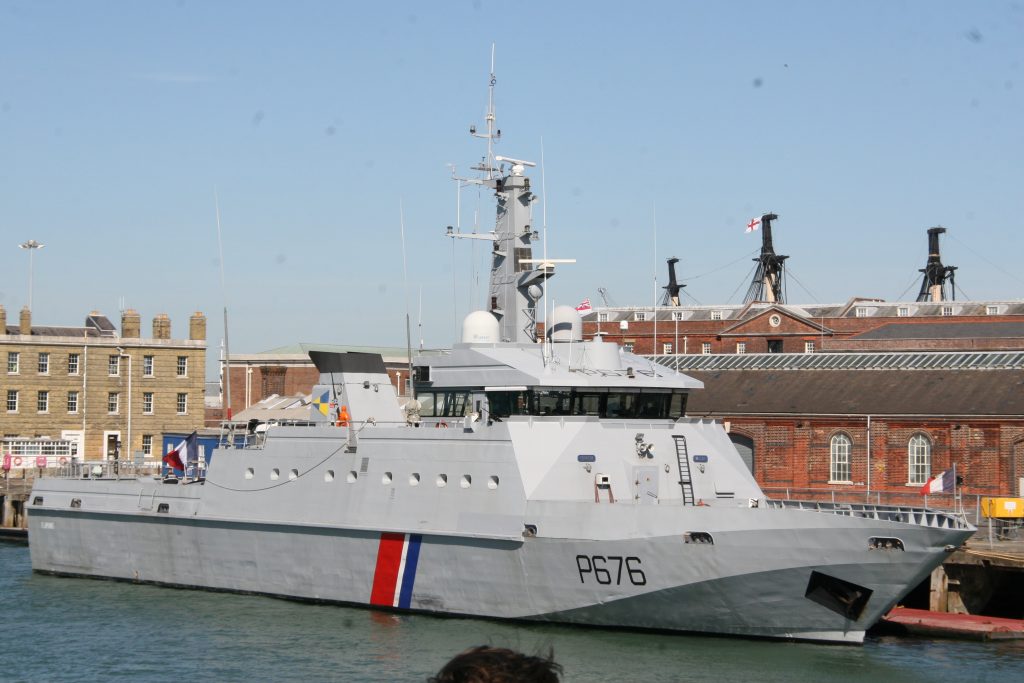




PSP Flamant, (P676) is a French Fisheries patrol vessel. the First of her class, she entered service in 1997. Three of these offshore patrol vessels are based in Cherbourg. The ship makes for an interesting contrast with Fulmar, which fulfills the same role off Saint Pierre and Miquelon.
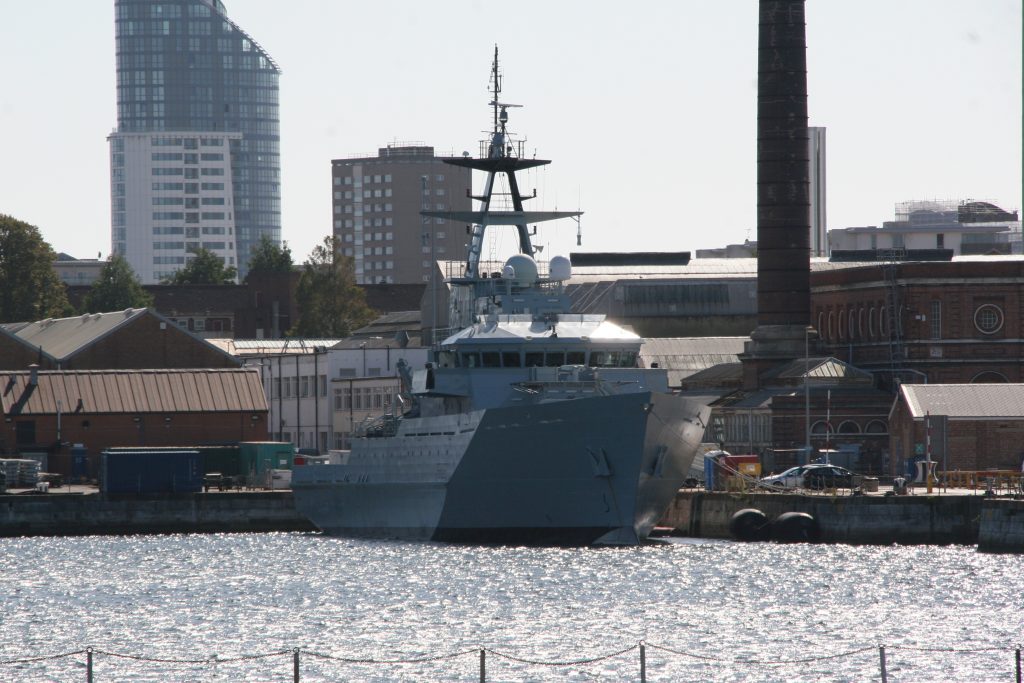
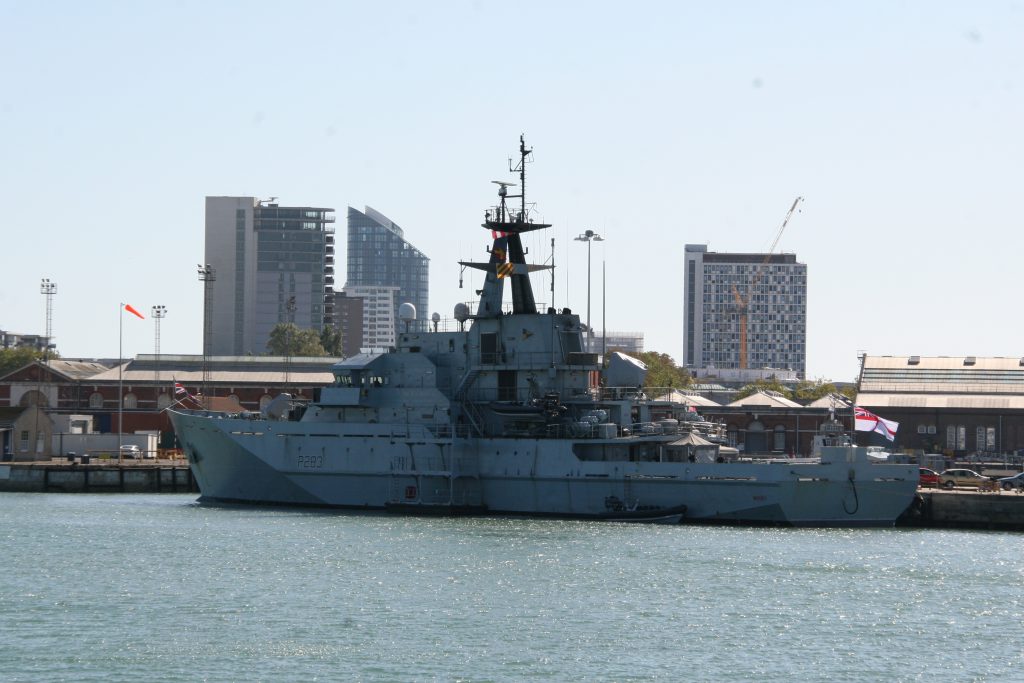
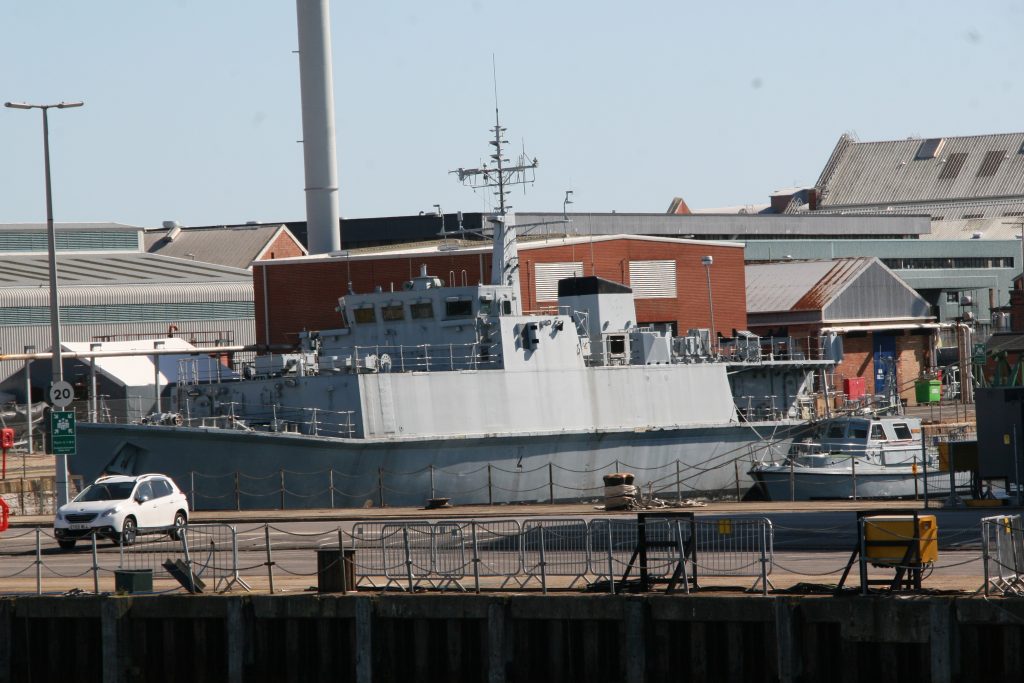
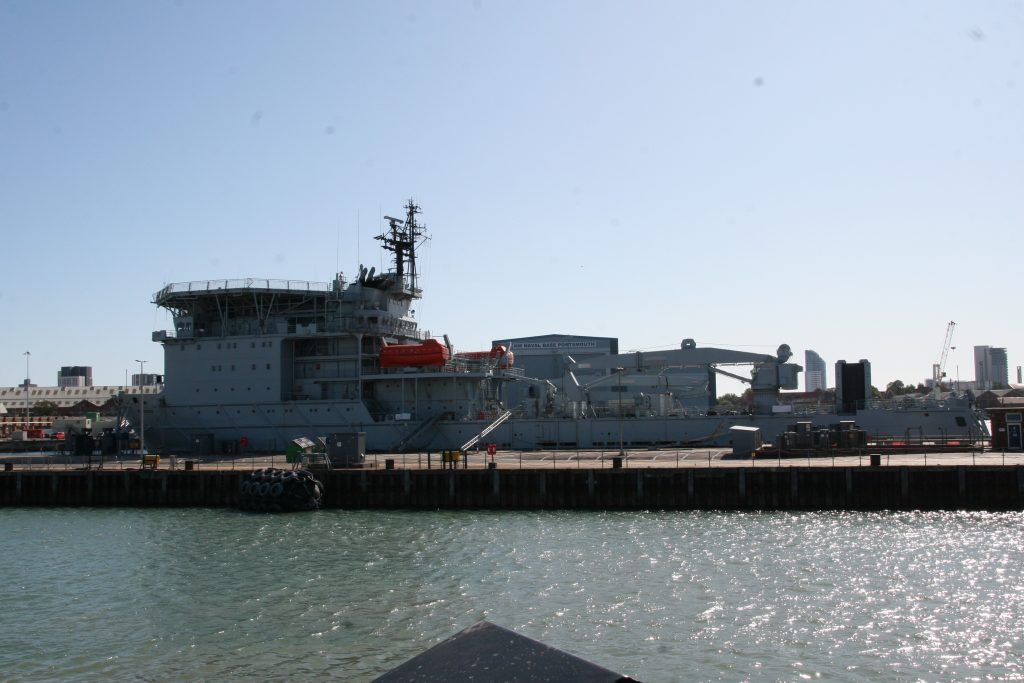
This one was photographed on a port visit to the Royal navy dockyard in Portsmouth, England. There will be more posts from that trip in the coming days.